Augmented satnav teams work together for safer flying
All satellite navigation is not created equal. Airliners and other safety-critical classes of users employ ‘augmented’ satnav signals, which possess additional precision plus ongoing reliability guarantees. These signals are generated by regional systems based around the globe. The teams responsible for them met recently at Delhi in India to coordinate their future development.
The 36th Satellite-based Augmentation Systems Interoperability Working Group (SBAS IWG) took place in Delhi last month, hosted by the Airport Authority of India.

For more than 20 years, the IWG has been coordinating the introduction of satellite-based augmentation systems for satnav – today there are 10 either in operation or active development. For this meeting of the group, SBAS developers and operators were joined for the first time by users of the systems, with representatives of airlines, aircraft makers and avionics manufacturers.
“Satellite-based augmentation systems deliver the necessary accuracy, integrity, availability and service continuity for aircraft to be able to rely on them though all phases of flight, from cruising in the air to being guided down for landing,” notes navigation engineer Didier Flament, head of ESA’s EGNOS and SBAS division, representing ESA at the SBAS IWG.

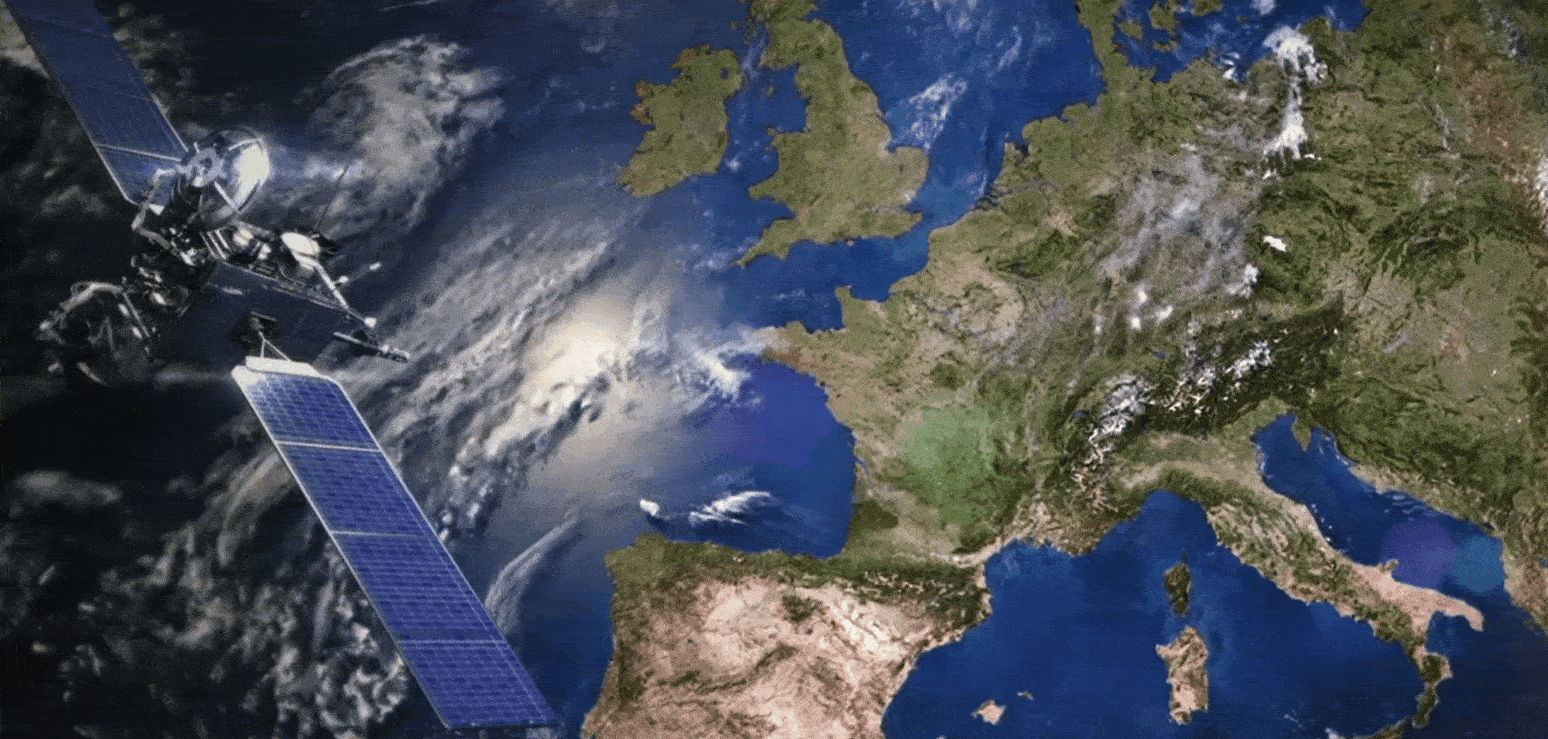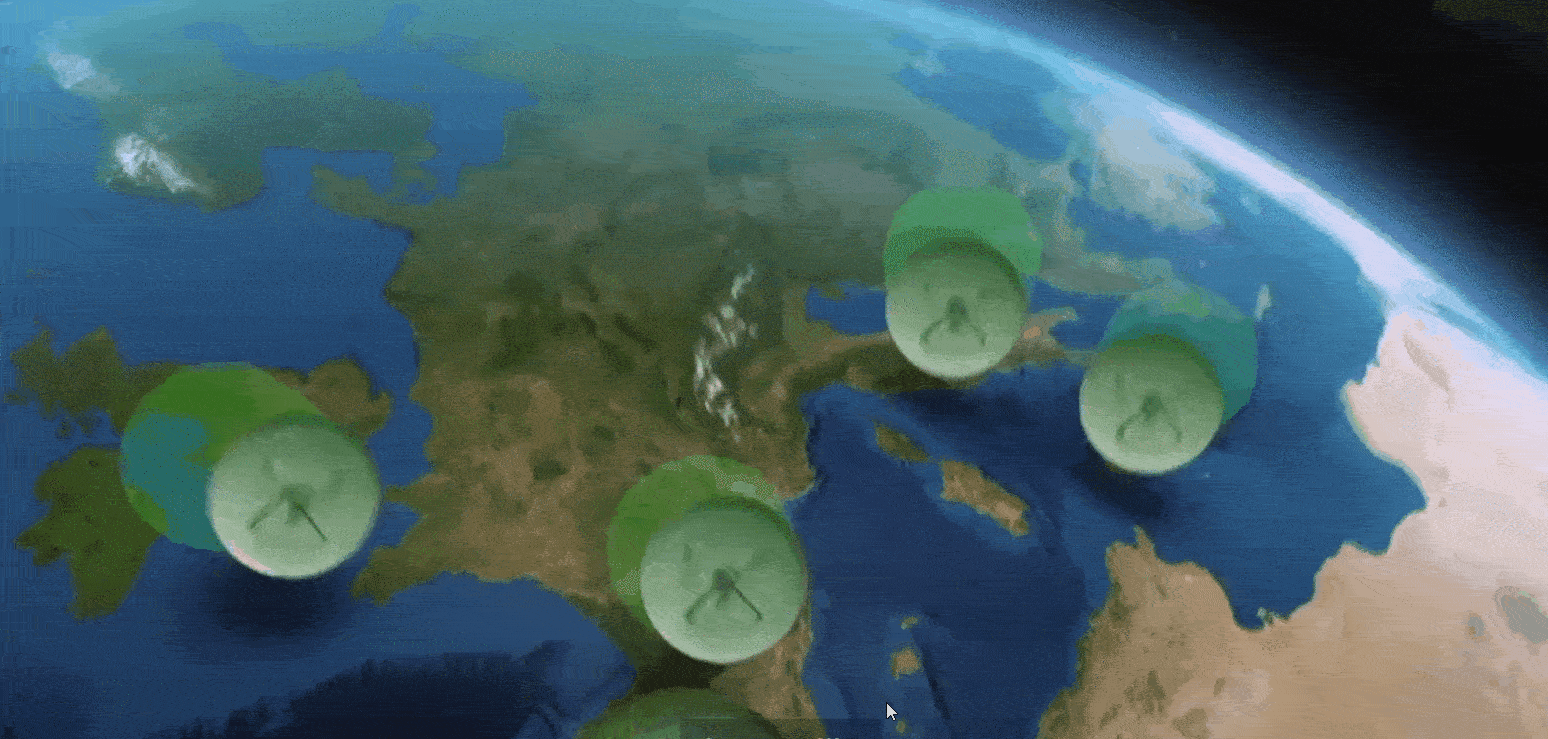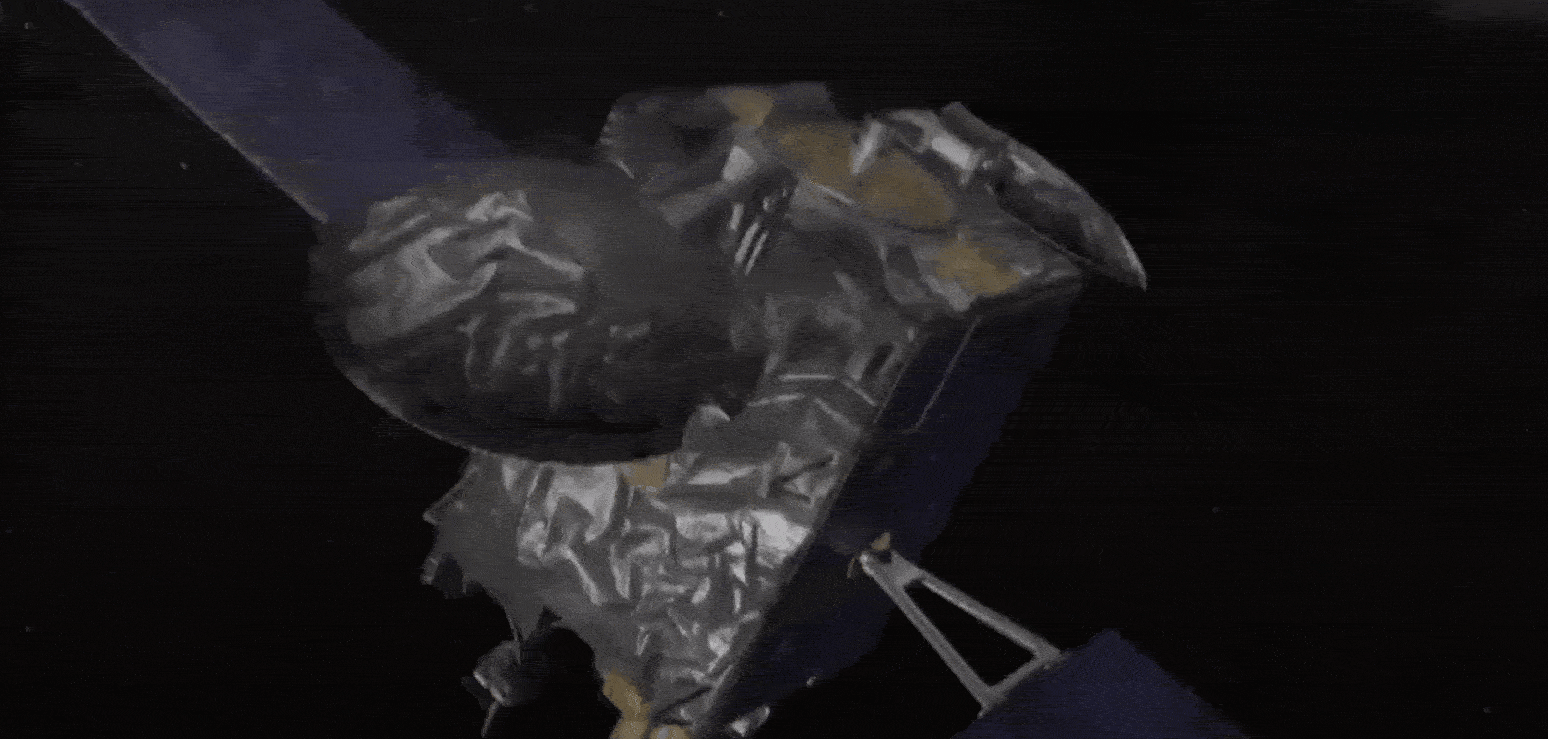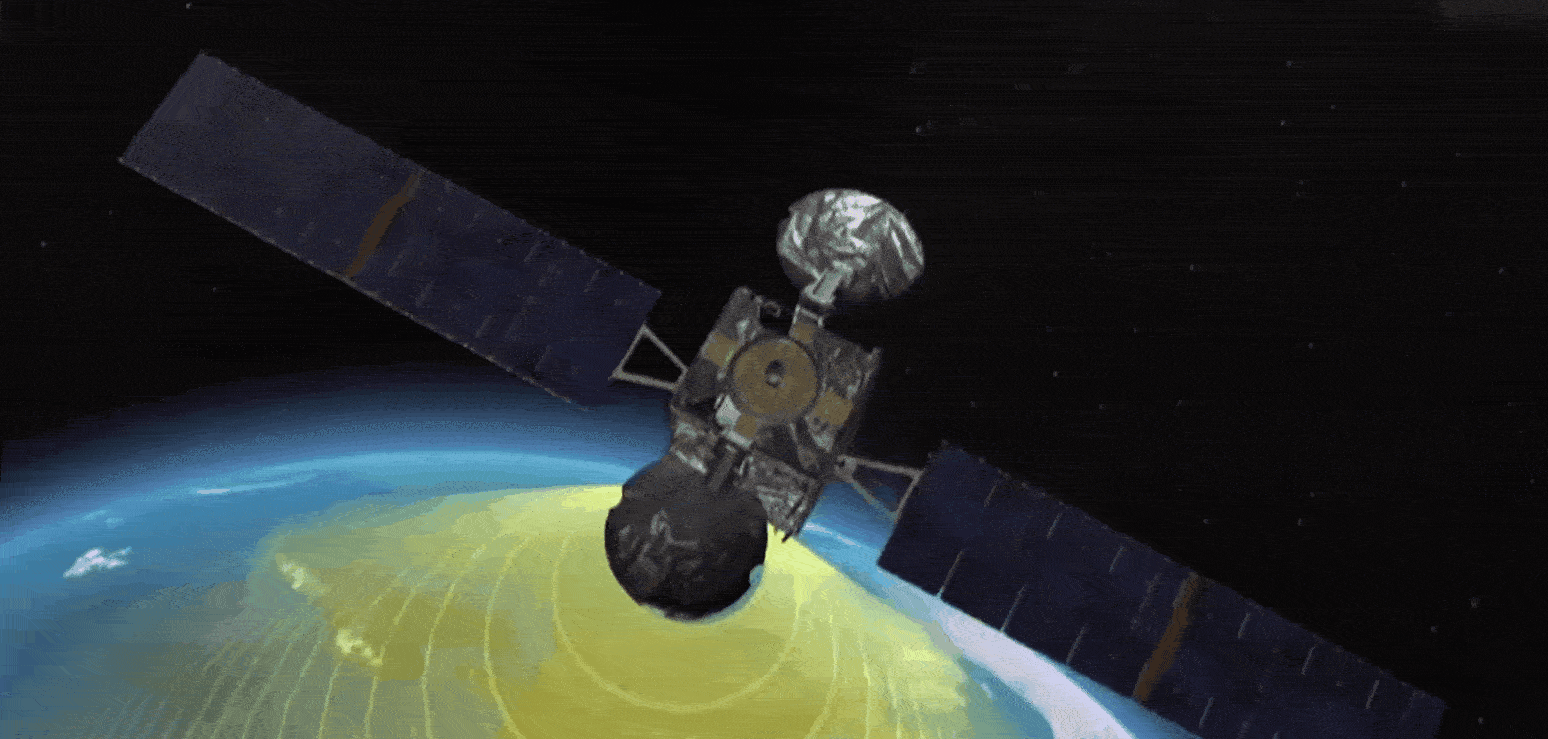
The US Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) and the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS) are leading examples of satellite-based augmentation systems (SBAS). They operate by using additional ground stations to enhance the accuracy and reliability of existing satnav services across given geographic regions.
Signal error measurements and integrity warnings highlighting reliability problems are then relayed to geostationary satellites for rebroadcast to users – messages available to any suitably equipped receiver. The resulting performance enhancements allow satnav to be employed for ‘safety of life’ services, especially aviation, but also any application requiring high precision.

The IWG heard that since their previous gathering six months earlier, a new regional SBAS program has been born : the Southern Positioning Augmentation Network, SPAN, covering Australia and New Zealand, represented at the meeting by Geoscience Australia and Land Information New Zealand.
Also covered at the 50-strong gathering was the progress of the four SBAS currently under definition or development: China’s Beidou SBAS, BDSBAS, represented by the China Satellite Navigation Office; South Korea’s KASS, represented by the Korea Aerospace Research Institute; the African and Indian Ocean SBAS, represented by the Agency for Aerial Navigation Safety in Africa and Madagascar (ASECNA); and the Russian Federation’s System for Differential Corrections and Monitoring (SDCM), represented by Russian Space Systems, RSS.
Current systems are mostly based around the US GPS system (except for SDCM using Russia’s Glonass and BDSBAS using China’s Beidou) but plans are being laid to move to a dual-frequency, multi-constellation version making use of Europe’s Galileo, China’s Beidou and Russia’s Glonass satnav systems later this decade. The corresponding version of Europe’s SBAS will be known as ‘EGNOS v3’.
The IWG is working to ensure that the future evolutions of all these systems will operate on a similar basis with common technical requirements, allowing the easy transition of continent-crossing air traffic from one system to another. This will be especially important in regions where system coverage overlaps.
The gathering also included an exchange of information on SBAS research and development, including applying SBAS to Europe’s railways.















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland