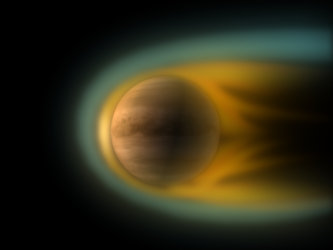
Comet-like ionosphere at Venus
The change in ionosphere of Venus during normal solar wind conditions (left) and reduced solar wind activity (right), as observed by ESA’s Venus Express spacecraft in August 2010. The yellow lines show a projection of the solar magnetic field lines as they interact with the ionosphere.
Venus Express follows an elliptical orbit around the planet once every 24 hours, passing within 250 km of the north pole and 66 000 km over the south pole. The observations were made on the nightside of the planet, when Venus Express was within 15 000 km of the centre of the planet. Although the spacecraft only took measurements within two Venus radii, the findings suggest that the ionosphere likely extends to even greater distances during periods of reduced solar wind intensity.
Read more: When a planet behaves like a comet