Prepping for radar vision
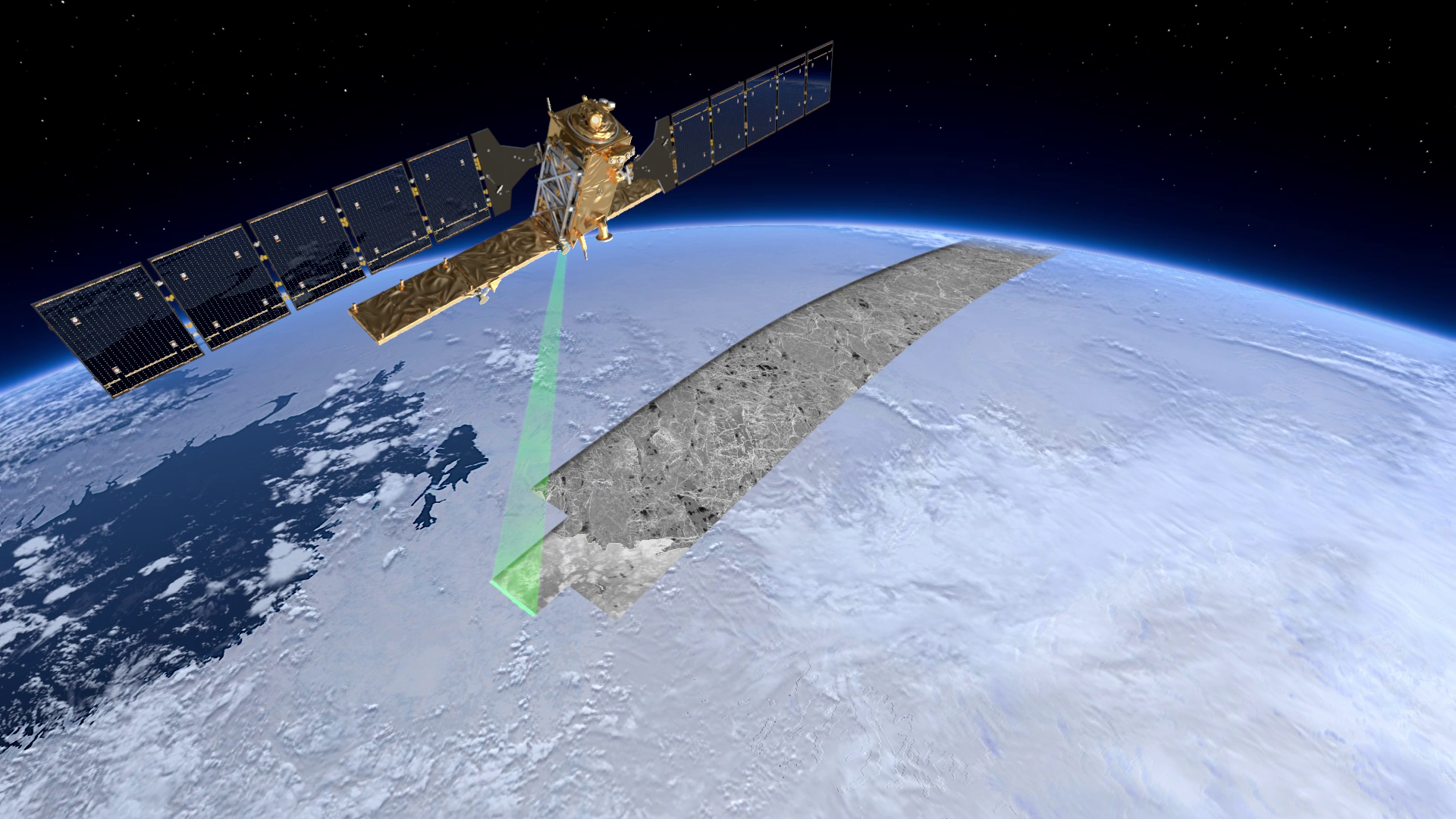
Sentinel-1A, Europe’s first satellite for Copernicus, is almost ready for launch on 3 April. Meanwhile, ESA is showing how its advanced radar will map ice, monitor subsidence and much more.
Marking a new era in Earth observation focusing on operational applications, Sentinel-1A is set to deliver timely imagery for numerous Copernicus services.
Carrying an advanced radar, it will scan Earth’s surface no matter what the weather and regardless of whether it is day or night.
In crisis situations, it will be used for rapid response to disasters such as floods and earthquakes. Its radar will routinely monitor shipping zones, map sea ice and provide information on winds and waves for marine traffic, track changes in the way land is being used, and monitor subsidence.


Access the video
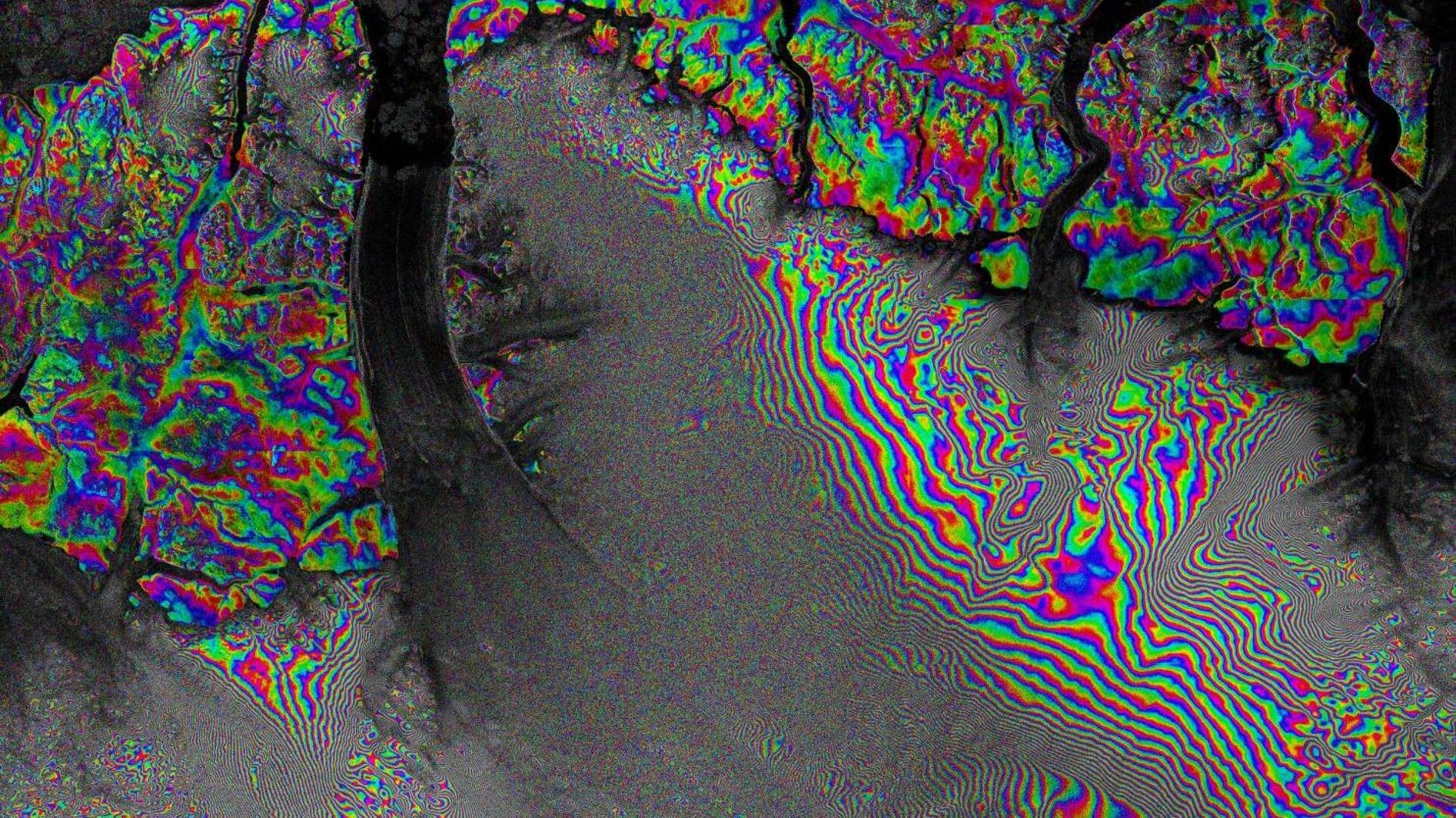
It will also track how glaciers move, as shown in the image above of Petermann Glacier in northwest Greenland.
So that users are fully prepared for the images Sentinel-1A delivers, Canada’s Radarsat-2 was recently programmed by MacDonald, Dettweiler & Associates to scan Earth’s surface using the same novel ‘interferometric’ wide-swath mode technique as Sentinel-1. Consequently, a suite of images was acquired over various sites.
As the most realistic Sentinel-1-like images to date, they show the performance and suitability of the new mission for classifying different types of sea ice, detecting ships and monitoring oil platforms.
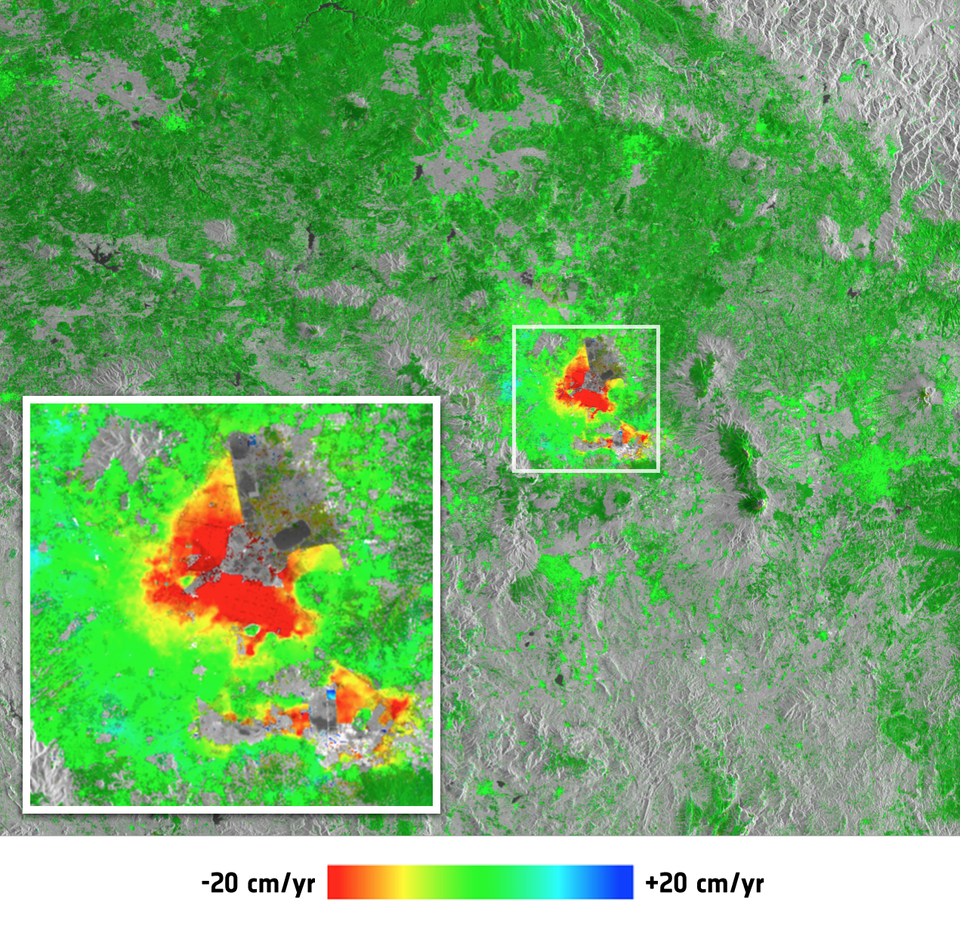
They also included image pairs to show changes in glaciers such as Petermann, and a ‘stack’ of 11 images to map surface subsidence in Mexico City.
The image of Petermann Glacier was derived from two images taken 24 days apart. It shows some stationary and slowly moving features, as well as some large areas of much faster-moving ice. The pattern’s fringes are widely spaced in the stationary areas and closer together in the centre of the glacier where the ice is moving much faster.
The wealth of data available through ESA’s Earth observation campaign data website is helping to pave the way for users to get the maximum out of the upcoming mission.
The Sentinel-1mission comprises two identical satellites for optimal global coverage and data delivery. Sentinel-1B will join Sentinel-1A in orbit next year.














 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland