Closed Loop Compartments
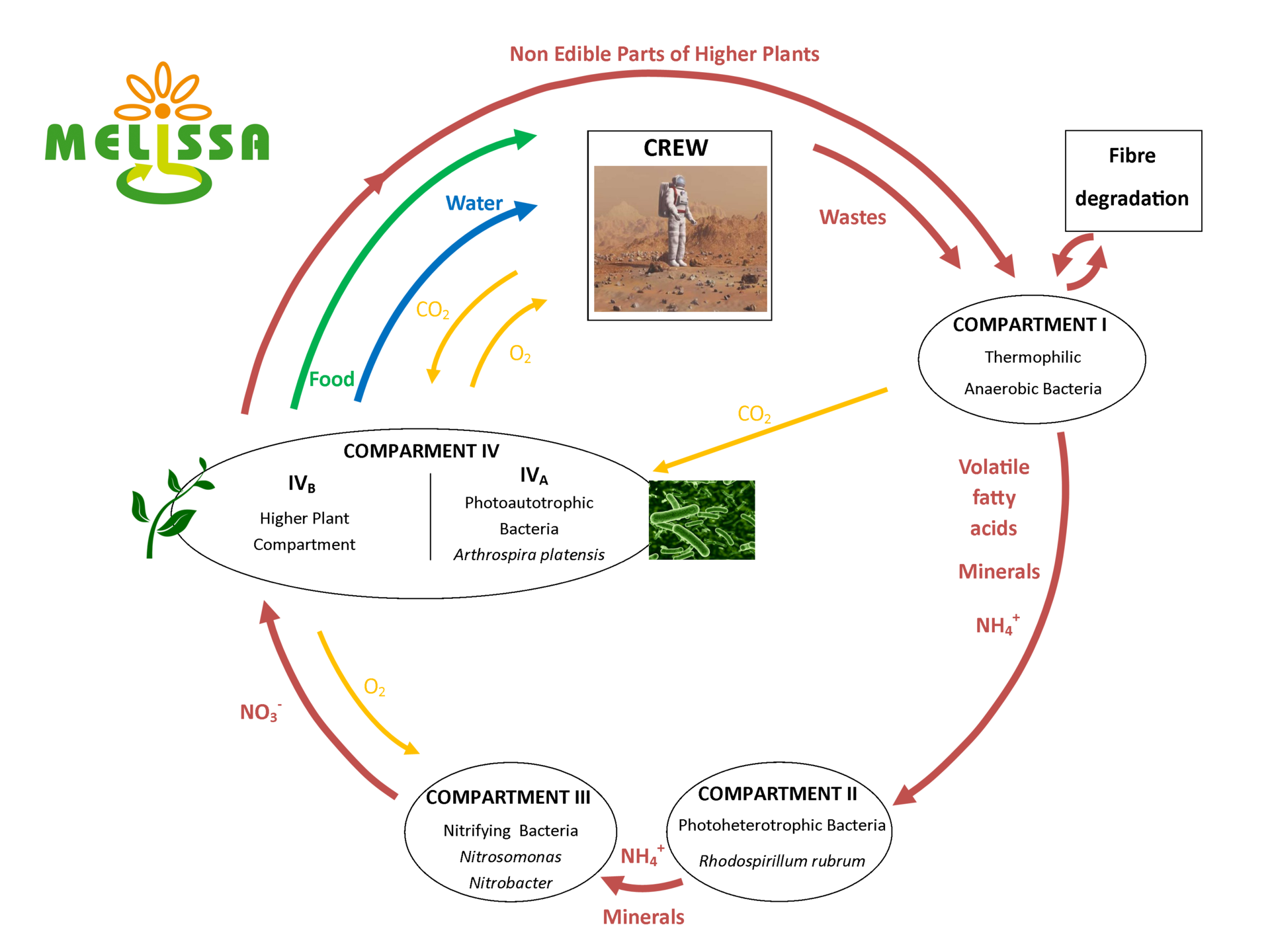
The MELiSSA loop has been structured as an assembly of unit-processes. These are the compartments, created to simplify the behaviour of an artificial ecosystem and allow a deterministic engineering approach. These compartments have specific functions assigned:


Access the video
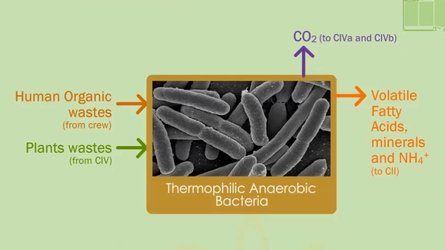
| CI | organic waste degradation & solubilisation by thermophilic anoxygenic bacteria |
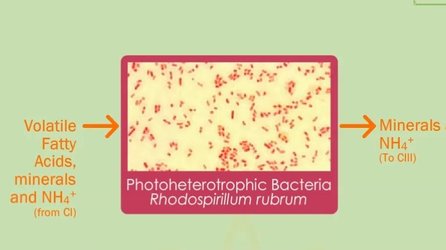
| CII | carbon compounds removal by photoheterotrophic bacteria |
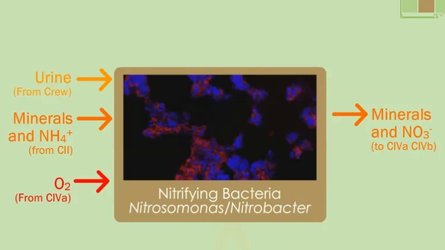
| CIII | Nitrification by nitrifying bacteria |
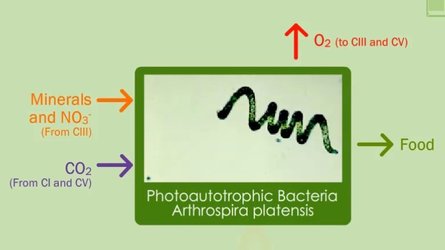
| CIVa | Food and oxygen production by photosynthetic bacteria |
| CIVb | Food, oxygen and water production by higher plants |
| CV | the crew |
The liquefying compartment is the first step in the MELiSSA loop and determines the fraction of organic wastes (e.g. non edible parts of plant material, paper) that can be recycled in the loop. Currently, research is performed to test physical/chemical treatment of the remaining fraction in order to further improve the biodegradability.
The CO2 that is produced in Compartment I is supplied to compartment IV (photosynthetic compartment). The volatile fatty acids and ammonia produced during the anaerobic fermentation process are fed to the photoheterotrophic anoxygenic compartment (Compartment II) where organic carbon should be transformed into inorganic carbon source.
Compartment III, or the nitrifying compartment, has as main purpose the conversion of ammonia into nitrates. Nitrate is the most suitable nitrogen source for compartment IVb (Higher Plant). The oxidation of ammonium is carried out by Nitrosomonas europaea, and the oxidation of nitrite by Nitrobacter winogradskyi, both forming part of a naturally attached biofilm within a fixed-bed reactor. The fixed nature of the biofilm is ideal in this case due to the low growth rate of the cells and its high conversion activity.
The photoautotrophic compartment (compartment IV) is responsible for the removal of CO2, generation of edible biomass as food supply, water recovery and for the regeneration of oxygen for the crew. This compartment is divided into a photoautotrophic cyanobacteria bacteria compartment, Arthrospira platensis, (compartment IVa) and a Higher Plant compartment (HPC) (Compartment IVb), which allows better CO2 assimilation rates and gives a more balanced diet for the crew. Although not finalised, nowadays a total of 32 crops are considered.














 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland