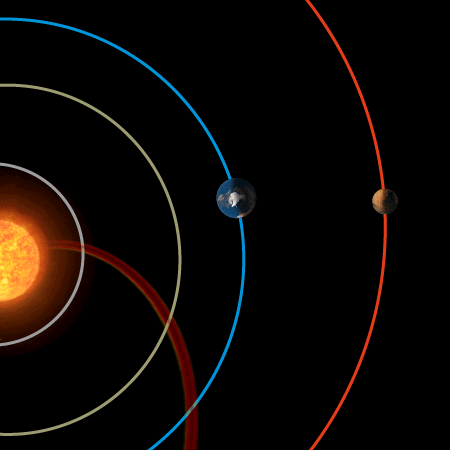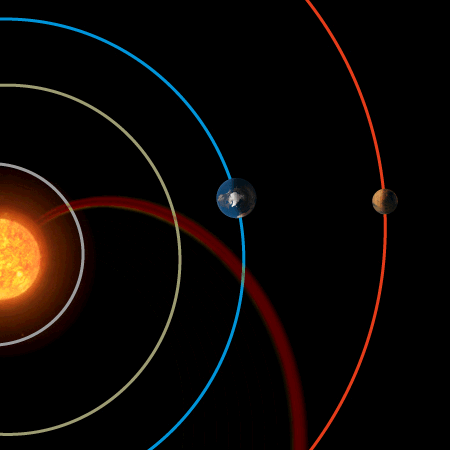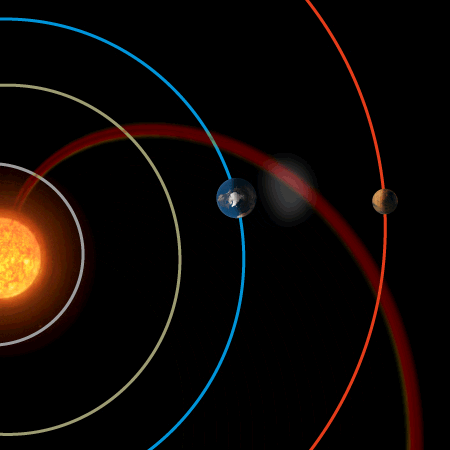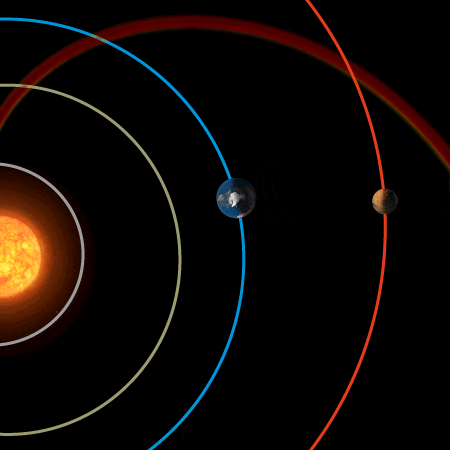
Earth’s magnetic field provides vital protection
A chance alignment of planets during a passing gust of the solar wind has allowed scientists to compare the protective effects of Earth’s magnetic field with that of Mars’ naked atmosphere. The result is clear: Earth’s magnetic field is vital for keeping our atmosphere in place.
The alignment took place on 6 January 2008. Using ESA’s Cluster and Mars Express missions to provide data from Earth and Mars, respectively, scientists compared the loss of oxygen from the two planets’ atmospheres as the same stream of solar wind hit them. This allowed a direct evaluation of the effectiveness of Earth’s magnetic field in protecting our atmosphere.
They found that while the pressure of the solar wind increased at each planet by similar amounts, the increase in the rate of loss of martian oxygen was ten times that of Earth’s increase.
Such a difference would have a dramatic impact over billions of years, leading to large losses of the martian atmosphere, perhaps explaining or at least contributing to its current tenuous state.

The result proves the efficacy of Earth’s magnetic field in deflecting the solar wind and protecting our atmosphere.
“The shielding effect of the magnetic field is easy to understand and to prove in computer simulations, thus it has become the default explanation,” says Yong Wei from the Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung, Germany, who led the study.
Now, by making measurements during a planetary alignment when the two planets were being hit by exactly the same part of the solar wind, the team have proved it in reality.
They now hope to extend their work by incorporating data from ESA’s Venus Express spacecraft, which also carries a sensor that can measure the loss of its atmosphere.
Venus will provide an important new perspective on the issue because like Mars, it has no global magnetic field, yet it is similar in size to Earth and has a much thicker atmosphere.
It will therefore provide unique data to help place the Earth and Mars results in context.
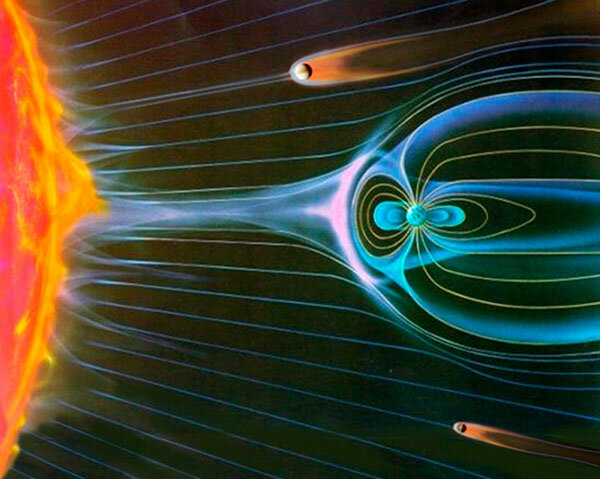
There are a number of upcoming planetary alignments that will provide good opportunities for such studies.
“For the next few months there is a good alignment between the Sun, Earth, Venus and Mars, and observations made by many spacecraft, including Mars Express, Venus Express and NASA’s STEREO solar observatory, will be analysed together,” says Olivier Witasse, ESA Mars Express Project Scientist.
Cluster will continue to play an important role in these studies, too. It is the only mission in near-Earth space capable of taking such measurements.
In addition, scientists are keen to observe how the increase in solar activity associated with the current solar cycle may affect the loss of atmospheric particles from all three planets.
“The European family of Solar System missions, with their unique observational capabilities, will play a vital role in studying this behaviour during the approaching maximum in solar activity,” says Matt Taylor, ESA Cluster Project Scientist.















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland