Overview
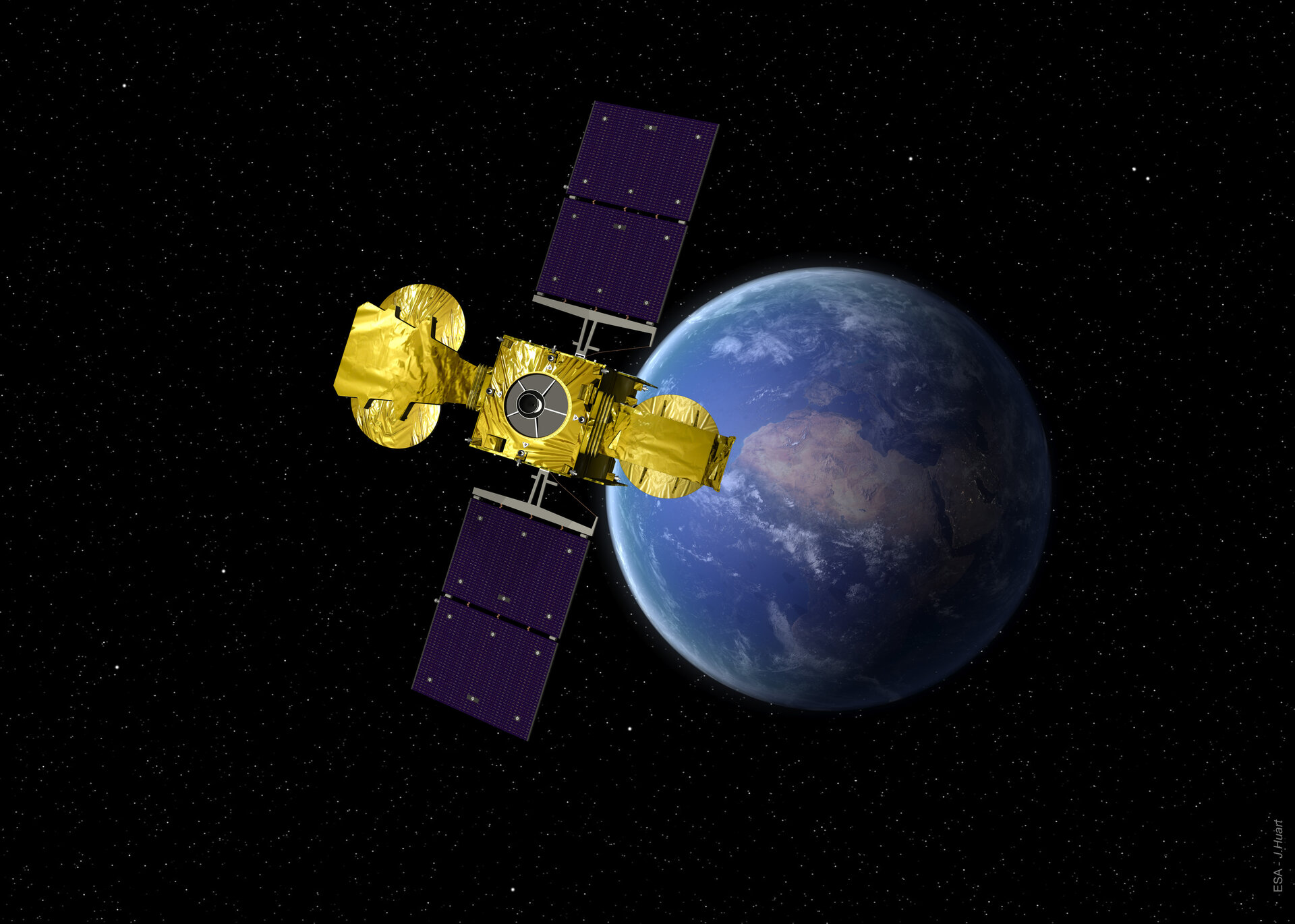
The Highly Adaptable Satellite is an advanced satellite system focused on high-speed internet connectivity for Europe.
Broadband from the sky
Operating across Ku- and Ka-band frequencies with advanced communication technology, Hylas-1 can pipe broadband through the sky to hundreds of thousands of previously underserved users while simultaneously broadcasting multiple standard and high-definition TV channels.

Ku-band and Ka-band are portions of the microwave spectrum: Ku-band is extensively used for satellite television broadcasting, while Ka-band is increasingly employed for broadband internet services.
Hylas-1’s wide Ku-band beam covers the whole of Europe. Its Ka-band antenna generates eight closely focused ‘spot beams’ for optimal frequency reuse, each providing coverage to a key European market. Bandwidth and power can be redistributed between beams to fulfil the changing needs of the market.
In partnership with business
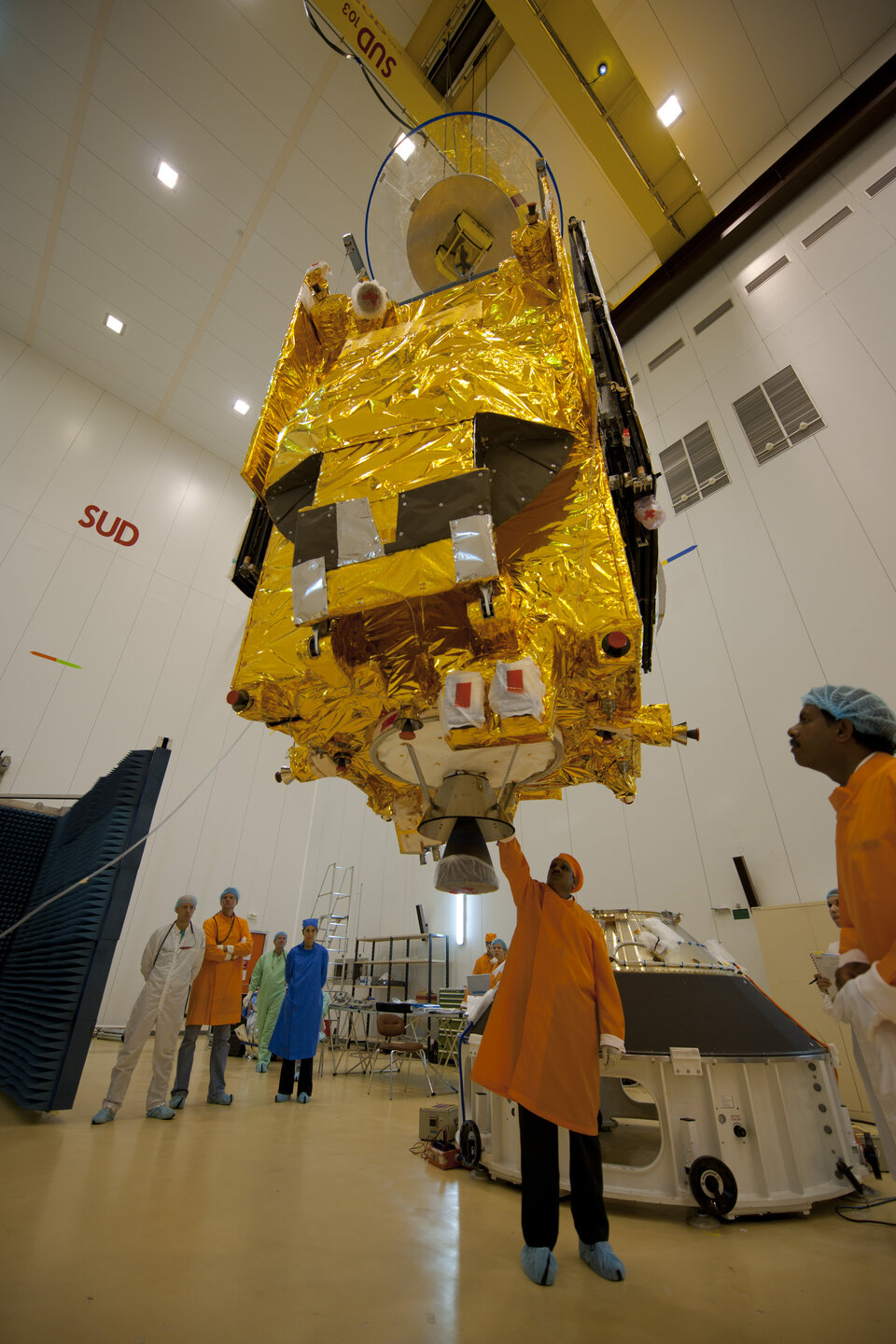
Hylas-1 is an innovative mission put together in a new way: it is ESA’s first public–private partnership resulting in a full satellite system. The commercial operator, UK-based Avanti Communications, has contributed most of the mission budget and will use the satellite to deliver broadband services to customers. ESA’s involvement focuses on Hylas-1's payload technology.
Joining forces with a commercial operator means that Europe’s advanced telecom technologies reach orbit much more rapidly and economically than otherwise. The Hylas-1 public–private partnership drives the technical state-of-the-art forward in space while efficiently serving a developing market.
| Hylas-1 facts and figures | |
|---|---|
| Launch date: | 26 November 2010 |
| Launch vehicle: | Ariane 5 ECA |
| Launch site: | Guiana Space Centre, Kourou, French Guiana |
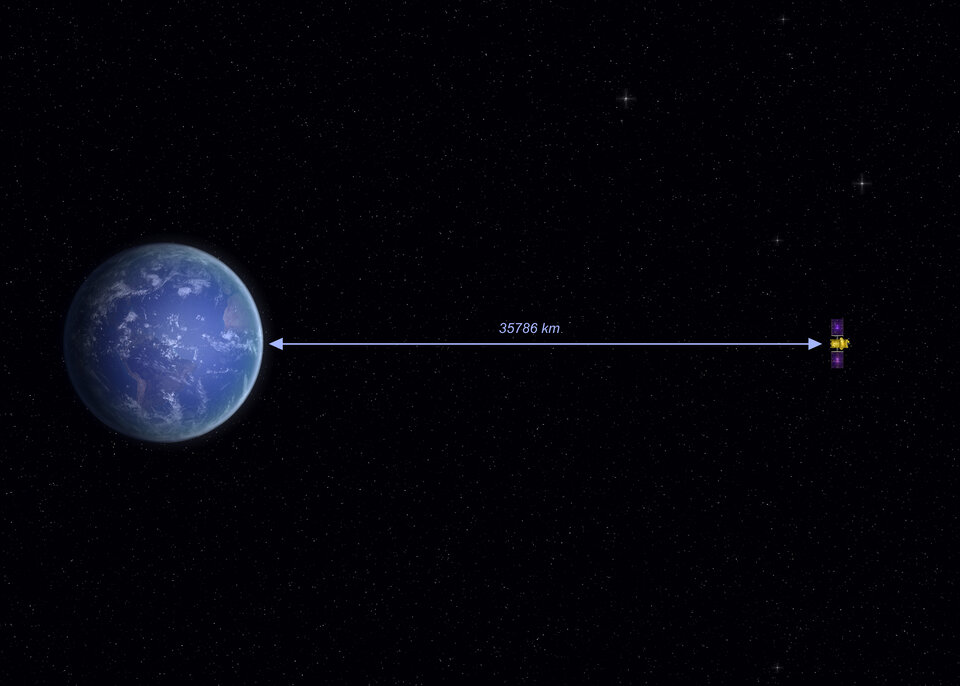
| Orbital location: | geostationary at 33.5°W |
| Operational lifetime: | 15 years |
| Payload: | repeaters: eight flexible Ka-band forward link transponders; one flexible Ka-band return link transponder; two flexible Ku-band transponders |
|
antennas: deployable 1.6 m-diameter Ku-band reflector antenna generating a linearly polarised shaped beam with European coverage; a single-feed-per-beam Ka-band antenna system with two elliptical antennas – each measuring 1.6 x 1.35 m – generating eight circularly polarised spot beams, each covering a key European market |
|
| Spacecraft bus: | ISRO I-2K (three-axis stabilised) |
| Launch mass: | 2242 kg (1109 kg dry mass) |
| Size: | 4.2 x 2.6 x 2.5 m; deployed solar array span 9.0 m; deployed antenna span 6.0 m |
| Power supply: | two Sun-tracking wings each comprising two (2.54 x 1.53 m) solar panels, made up of triple-junction gallium arsenide cells; two batteries each comprising 20 lithium-ion cells with 32 Ah capacity |
| Satellite control centre: | Inmarsat HQ, East London, UK |
| Network operations centre: | Avanti Communications HQ, London, UK |
| Gateway stations: | primary: Goonhilly (UK); back-up: Land’s End (UK) |















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland




























