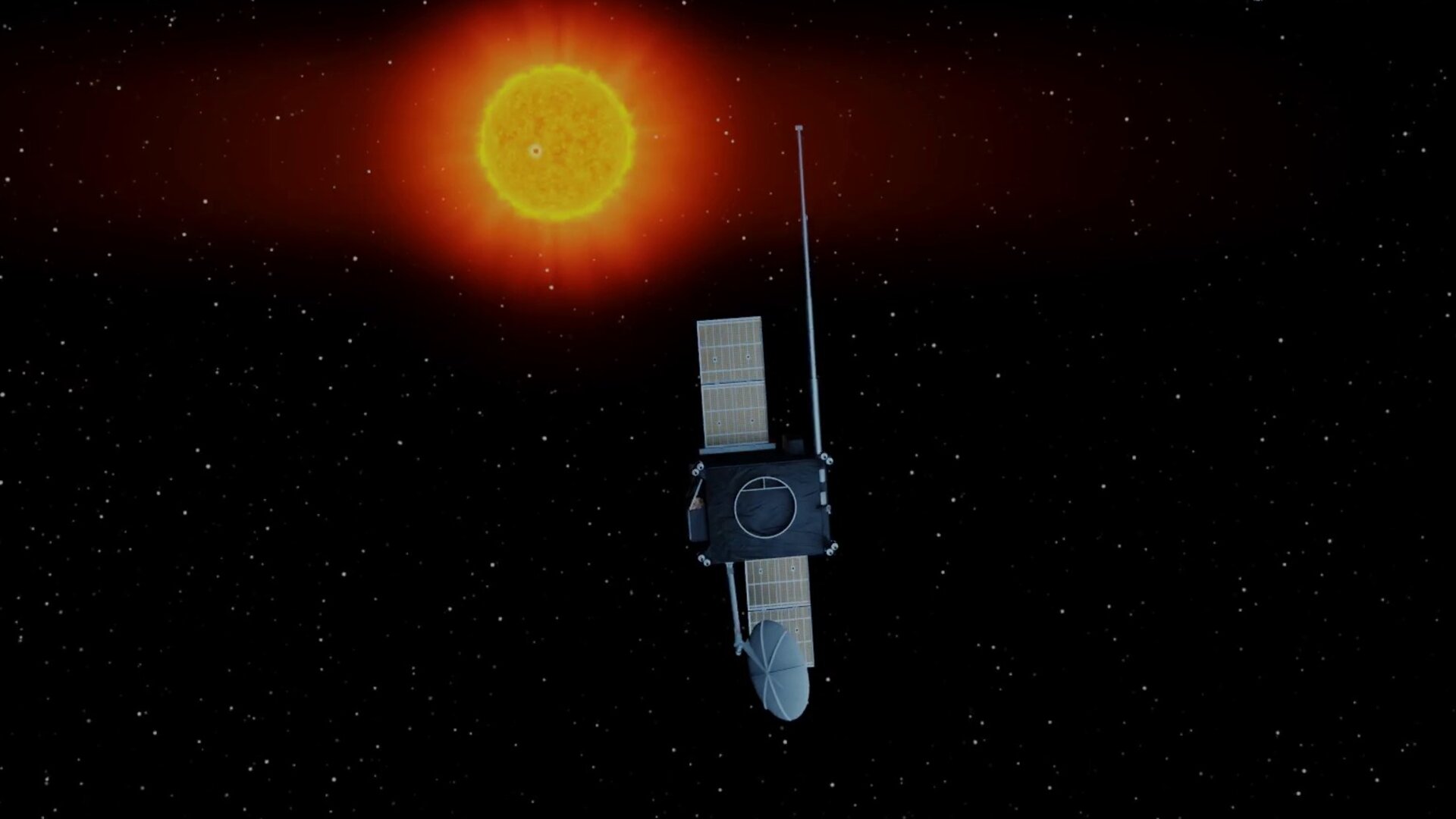
ESA Vigil overview
Living near a star is risky business, and positioning a spacecraft near the Sun is a very good way to observe rapidly changing solar activity and deliver early warning of possibly harmful space weather. With the mission formerly known as "Lagrange", but now renamed Vigil, ESA will do just that.
On most days, our normally calm Sun goes about its business, delivering a steady and predictable amount of heat and light that keeps planet Earth and its humans ticking.
But just as the Sun drives weather on Earth, solar activity is responsible for disturbances in our space environment, dubbed ‘space weather’.
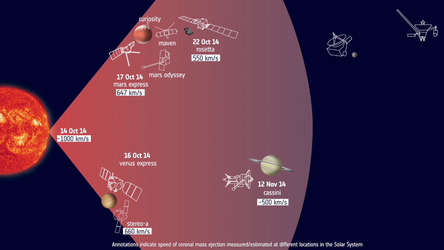
Besides emitting a continuous stream of electrically charged atomic particles, the Sun periodically sneezes out billions of tonnes of material threaded with magnetic fields in colossal-scale ‘coronal mass ejections’.
These immense clouds of matter usually miss Earth, but if one reaches us it can disrupt Earth’s protective magnetic bubble and upper atmosphere, affecting satellites in orbit, navigation, terrestrial power grids, and data and communication networks, among other effects.
Getting a view of the action
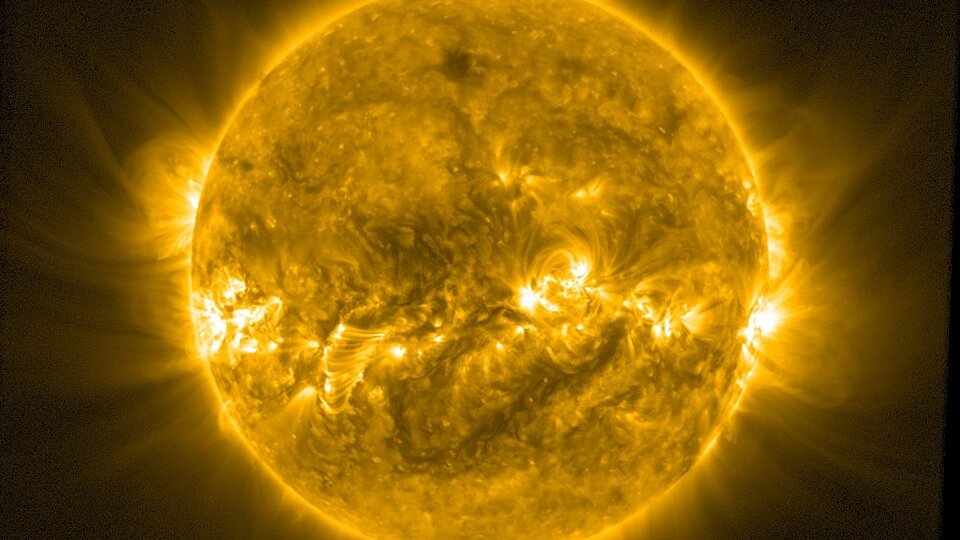

Obtaining warnings of such events would be immensely helpful: a recent ESA study estimated the potential impact in Europe from a single, extreme space weather event could be about €15 billion.
As just one example, even moderate space weather events can affect electrical power grids that supply electricity to homes, hospitals and schools. Improved warning times for larger events would allow grid operators to take measures to protect their networks and ensure continued power delivery.
“One of the best ways to observe rapidly changing solar activity is to position a dedicated spacecraft slightly away from our direct line to the Sun, so that it can observe the ‘side’ of our star before it rotates into view,” says Juha-Pekka Luntama, responsible for space weather at ESA’s mission control centre, Darmstadt, Germany.
Virtual points in space
One of these, the 5th Lagrange point, lags 60º degrees behind Earth in its orbit – an ideal location for monitoring mass ejections from the ‘side’ so as to give early warning and better estimates of the speed and direction.
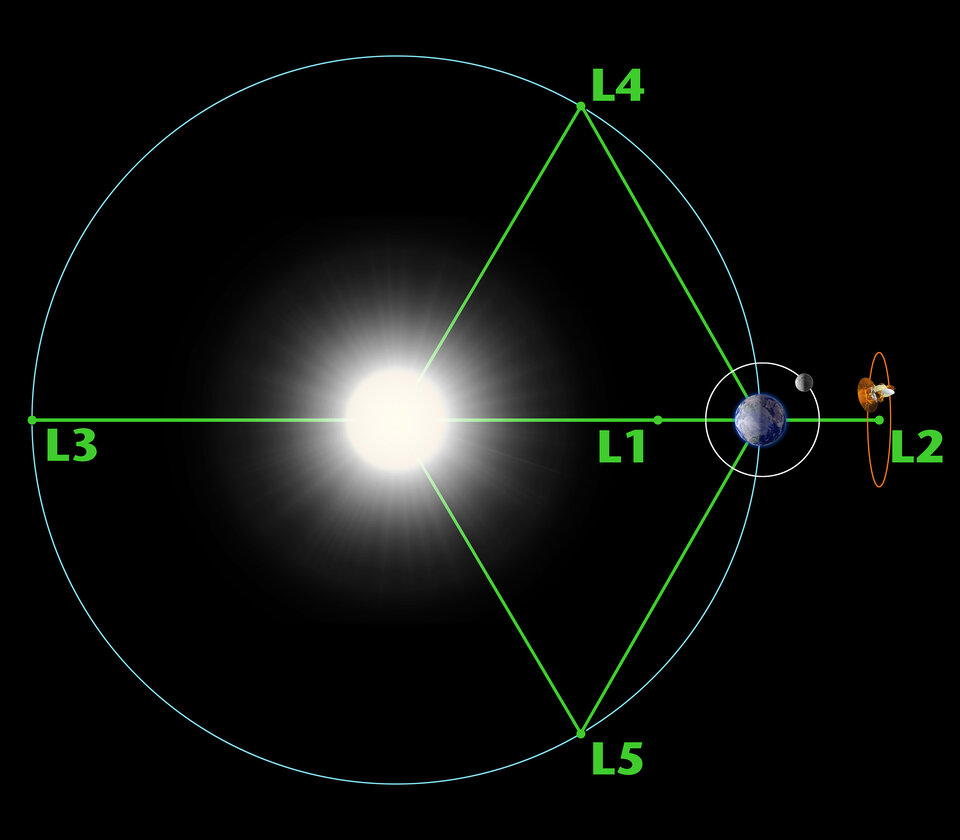
“L5 is an excellent spot for a future ESA space weather mission because it gives advance views of what’s happening at the Sun,” says Juha-Pekka.
“The spacecraft would provide crucial data that will help us spot Earth-arriving ejections, improve our forecasts of the arrival time at Earth and provide advance knowledge of active regions on the Sun as they rotate into view.”
First-ever mission to L5
Today, ESA began studies to examine exactly this concept. Four European industrial and scientific consortiums including leading experts on space systems and instrument design will develop concepts for flying a mission to L5.
Based on the results, ESA will select a final design in about 18 months.
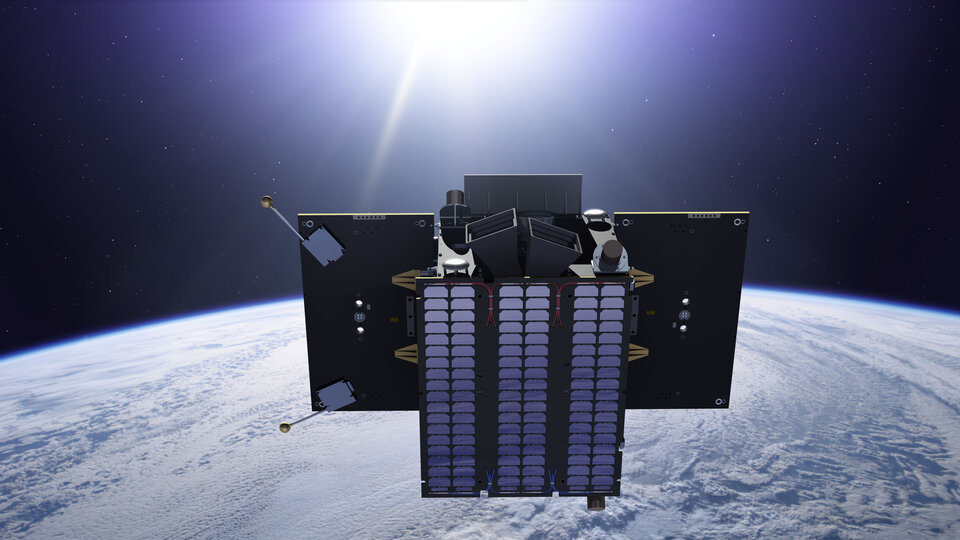

This space weather mission would provide data for operational applications such as forecasts and nowcasts of solar activity.
These are part of ESA’s Space Weather Service Network, which will issue warnings and alerts to scientific, commercial and civil customers when solar activity poses any risk to critical civil and economic activities.















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland