A
Aberration
Property of an optical system that causes an image to have certain easily recognisable flaws. Aberrations are caused by geometrical factors such as the shapes of surfaces, their spacing, and alignments. Image problems caused by factors such as scratches or contamination are not called aberrations.
Absolute zero
The lowest temperature ever reachable in the Universe: 0 kelvin (0K), equivalent to minus 273.15 degrees Celsius (-273.15 °C). In laboratories on Earth physicists can get very close to that temperature, but it is impossible to achieve the absolute zero.
Absorption
Decrease in intensity of radiation, when it crosses a material medium, as a consequence of an interaction between the radiation and the material medium.
Abundance
Relative number of atoms of a particular element, or isotope of an element, in the chemical composition of a single substance or object.
Accelerometer
Oscillatory mechanical system measuring the acceleration of the body to which it is attached.
Accretion (disc, zone)
Process whereby small particles of matter accumulate and create larger bodies under the influence of their mutual gravitational attraction or as a result of chance collisions.
Active galactic nucleus (AGN)
Central region of a galaxy in which considerable energy is generated by processes other than those present in normal stars. The energy generated by the nucleus may outshine all the other stars in the galaxy. Most astronomers believe that at the centre of an AGN lies a supermassive black hole.
Active galaxy
A galaxy which releases large amounts of energy from its centre, the active galactic nucleus. The central engine of an active galaxy probably is a supermassive black hole. Seyfert galaxies, quasars and blazars are active galaxies.
Aeronomy
The study of the atmosphere of a planet, with particular attention to the composition, properties and motion of atmosphere constituents.
Aerosol
A gaseous suspension of ultramicroscopic particles of a liquid or a solid.
Aerosol collector
An instrument that collects aerosols and analyzes their composition.
Algol
Best known variable star, varying in brightness from about 2.2 to 3.5 magnitudes over a period of approximately 69 hours. It is in fact a binary system in which the two stars regularly cross in front of each other as viewed from Earth. Also known as the Demon Star.
Alignment
Process of mounting optical elements and adjusting their positions and orientations so that light follows exactly the desired path through the instrument and each optical element performs its function as planned.
Altitude
Height in space of an object or point relative to sea level or ground level.
Angstrom
Unit to measure length, sometimes used to measure the wavelength of light. (See also Electromagnetic spectrum). 10 000 Angstroms correspond to 1 micron.
Anisotropy, Inhomogeneity (in the cosmic microwave background) Very small patches in the sky where the temperature of the cosmic microwave background is slightly different to the average; these temperature variations are of the order of microkelvin.
Antenna (high gain, low gain)
An aerial for receiving or transmitting radio signals. A high gain antenna is highly focused, whereas a low gain antenna receives or transmits over a wide angle.
Antimatter
The 'opposite' to ordinary matter. For every particle of ordinary matter there is an almost identical antiparticle of antimatter: protons and antiprotons; electrons and positrons... the particle's mass is exactly the same as its antiparticle's mass, but their electrical charges - and other fundamental properties - are opposite. When a particle meets its antiparticle, they annihilate each other.
Aperture
Opening that allows light to fall onto an instrument's optics.
Aphelion
The point on a planet's elliptical orbit at which it is furthest from the Sun.
Apocentre
The point on a spacecraft's orbit at which it is furthest away from the body it is orbiting.
Apogee
The most distant point from Earth on a satellite's orbit.
Arcmin, arcsec
The size of an object in the sky can be measured by the angle that it covers when viewed from Earth. The full circle has 360 degrees. An arcmin is 1/60 of a degree; an arcsec is 1/60 of an arcmin or 1/3600 of a degree. The diameter of the full Moon is about one-half of a degree or 30 arcmin.
Argon
A chemical element, (symbol Ar, atomic number 18).
Ariane (4, 5) rockets
European launcher family (Ariane 4 and Ariane 5) developed by the European Space Agency. Launched from Kourou, French Guiana, flights are commercialised and operated by the Arianespace company.
Asteroid
One of billions of rocky objects, less than 1000 km in diameter, which orbit the Sun. Also known as minor planets. Thought to be planetesimals leftover from the formation of the planets. The first asteroid (Ceres) was discovered by Giuseppe Piazzi in 1801. More than 10 000 asteroids have so far been discovered and given permanent identification numbers. The largest asteroid is 2001 KX76 with a diameter of at least 1200 km.
Asteroid belt
Region between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter which is populated by billions of asteroids.
Astigmatism
Failure of an optical system, such as a lens or a mirror, to image a point source of light as a single point.
Astrometry
The branch of astronomy concerned with measuring the positions of celestial bodies, such as stars and galaxies, and their real and apparent motions.
Attitude
Orientation of the spacecraft's axes relative to Earth.
Astronomical Unit (AU)
1 Astronomical Unit corresponds to the distance separating the Earth from the Sun. 1AU=150 million km.
Astronomy
Study of the space beyond the Earth and of its contents.
Astrophysics
Study of the physical nature of the Universe, its objects and the composition of the space between them.
Atmosphere
Layer of gases surrounding a star or planet.
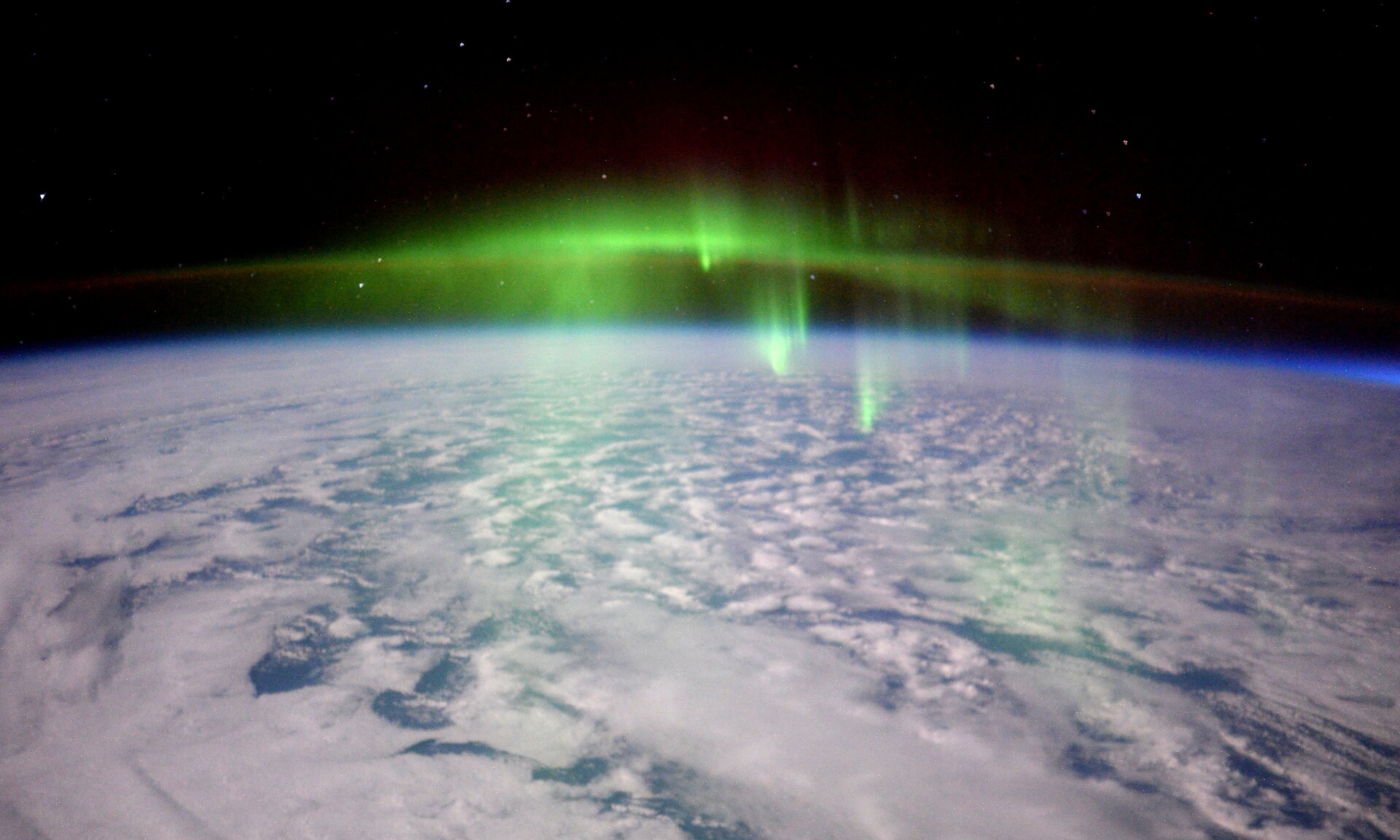
Aurora
Illumination of the night sky, caused when electrons and protons from space collide with atoms and molecules of air in the Earth's upper atmosphere. Satellite observations usually show them as rings centred on the planet's magnetic poles. Popularly known as the Northern and Southern Lights. Various types of aurora are also found on Jupiter, its moon Ganymede, and Saturn.















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland