SMART-1 impact flash and debris: crash scene investigation
Timing, location, detection of a flash and of ejected material, and a firework generated by the lunar impact of ESA's SMART-1, are the latest results gathered thanks to the ground observation campaign of this historical event.
"The successful capture of the SMART-1 impact from Earth raised a substantial interest in the amateur and professional astronomical community. They started to reanalyse the available data, to repeat observations of the impact site and to share the results worldwide as a family", says Pascale Ehrenfreund, coordinator of the SMART-1 impact ground observation campaign.
Where did SMART-1 impact the Moon?
"From the various observations and models, we try to reconstruct the 'movie' of what happened to the spacecraft and to the Moon surface," says ESA SMART-1 Project scientist Bernard Foing. "For this lunar 'Crash Scene Investigation', we need all possible Earth witnesses and observational facts."
The actual SMART-1 impact took place on 3 September 2006 in the course of the spacecraft’s 2890th orbit around the Moon. SMART-1 sent its last signals to Earth at 07:42:21:759 CEST (05:42:21:759 UT), and the JIVE radio telescope from Hobart, Tasmania, measured a loss of signal a few moments later, at 07:42:22.394 CEST (05:42:22.394 UT).

These times are remarkably in agreement with the last SMART-1 flight dynamics predictions of 3 September at 07:42:20 CEST (05:42:20 UT), in the location at 46.20º West longitude and 34.4º South latitude.
This is also in agreement with the coordinates newly derived from the position of the infrared impact flash observed by the Canada-France-Hawaii telescope (CFHT).

Extensive data processing is now going on to specify the topography of the impact site.
From a preliminary analysis of the topographic stereo data available and earlier maps built with SMART-1 data, the satellite should have hit the Moon in the ascending slope of a mountain about 1.5 kilometres high, above the Lake of Excellence plain.
What happened? Dust after the flash

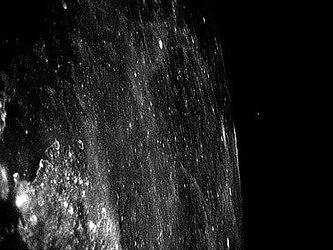
To determine what part of the flash comes from the lunar rock heated at impact or from the volatile substances released by the probe, it is important to obtain measurements in several optical and infrared wavelengths, in addition to the CFHT observations (2.12 microns).

From a detailed analysis of the CFHT infrared movie of the variations after the flash, a cloud of ejected material or debris travelling some 80 kilometres in about 130 seconds has been detected by observer Christian Veillet, Principal Investigator for the SMART-1 impact observations at CFHT.

"It seems that some ejecta or debris made it across the mountain. This is good news to search for the ejecta blanket" says Foing." We might also see the 'firework' expansion of gas and debris that has bounced after impact from the spacecraft."
Some SMART-1 campaign amateurs report that they may have observed the optical flash in their own data, and a possible impact afterglow. "We call for observers to search for the crater and ejecta blankets from SMART-1, in particular using visible or infrared imagery, or even to look at spectroscopic anomalies at the impact site," added Foing. "We also call all observers to send us their reports, thanking them for engaging in the SMART-1 adventure".
Note to editors
The five radio telescopes involved in the SMART-1 observations and coordinated by the Joint Institute for VLBI (Very Long Baseline Interferometry) in Europe (JIVE), are: the Medicina (INAF) 32- metre antenna in Italy, the Fortaleza (ROEN) 14-metre antenna in Brazil, the German-Chilean TIGO (BKG) 6-metre antenna in Chile, the Mount Pleasant Observatory of the University of Tasmania (Australia) and the Australia Telescope Compact Array (CSIRO).
The SMART-1 impact observation campaign involved a core of participating telescopes, including: the South African Large Telescope (SALT), the Calar Alto observatory in Andalucia, Spain, the ESA Optical Ground Station (OGS) at Tenerife, Spain, the TNG telescope in La Palma, Canary Islands, Spain, the CEA Cariri observatory in Brazil, the Argentina National Telescope, the Florida Tech Robotic telescopes at Melbourne FL and Kitt Peak, MSFC lunar meteor robotic telescopes, Houston 1m, Big Bear Solar Observatory, MDM telescopes at Kitt Peak, NASA IRTF, the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope, the Japanese Subaru Auxiliary telescopes on Hawaii, the ODIN space observatory. We acknowledge also support from Nottingham University, and the USGS.
Reports on data gathered by other observatories that joined the campaign will follow on this site.
For more information
Bernard H. Foing, ESA SMART-1 Project Scientist
Email: bernard.foing @ esa.int
Pascale Ehrenfreund, SMART-1 ground-based impact campaign coordinator, Leiden University, The Netherlands
Email: pascale @ strw.leidenuniv.nl















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland