Geos principal features
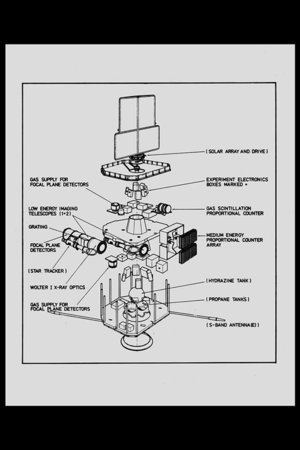
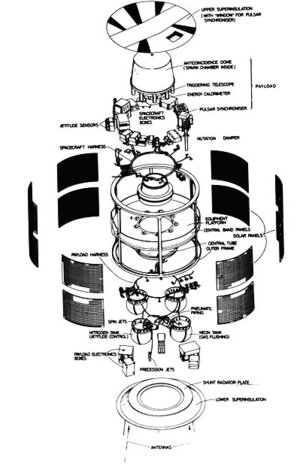
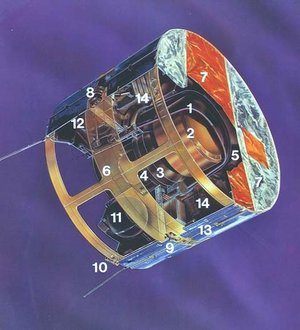
Principal features of ESA's Geos spacecraft. Geos was designed for geostationary orbit to study the particles, fields and plasmas of the Earth's magnetosphere using seven instruments provided by ten European laboratories. Because of its unique orbit and the sophistication of its payload, Geos was selected as the reference spacecraft for the worldwide 'International Magnetospheric Study'. Unfortunately, Geos-1 was left in a low transfer orbit following launch on 20 April 1977 because of a problem with its US Delta launcher. As a result, the Qualification Model was launched as Geos-2 on 14 July 1978 with an identical payload and successfully reached the planned orbit. In spite of its orbit, Geos-1 made a significant contribution to IMS, and its mission formally ended on 23 June. Geos-2 was highly successful, creating a huge database for magnetospheric studies and plasma research in general. [Image Date: 1976] [98.06.011-001]