
Science & Exploration
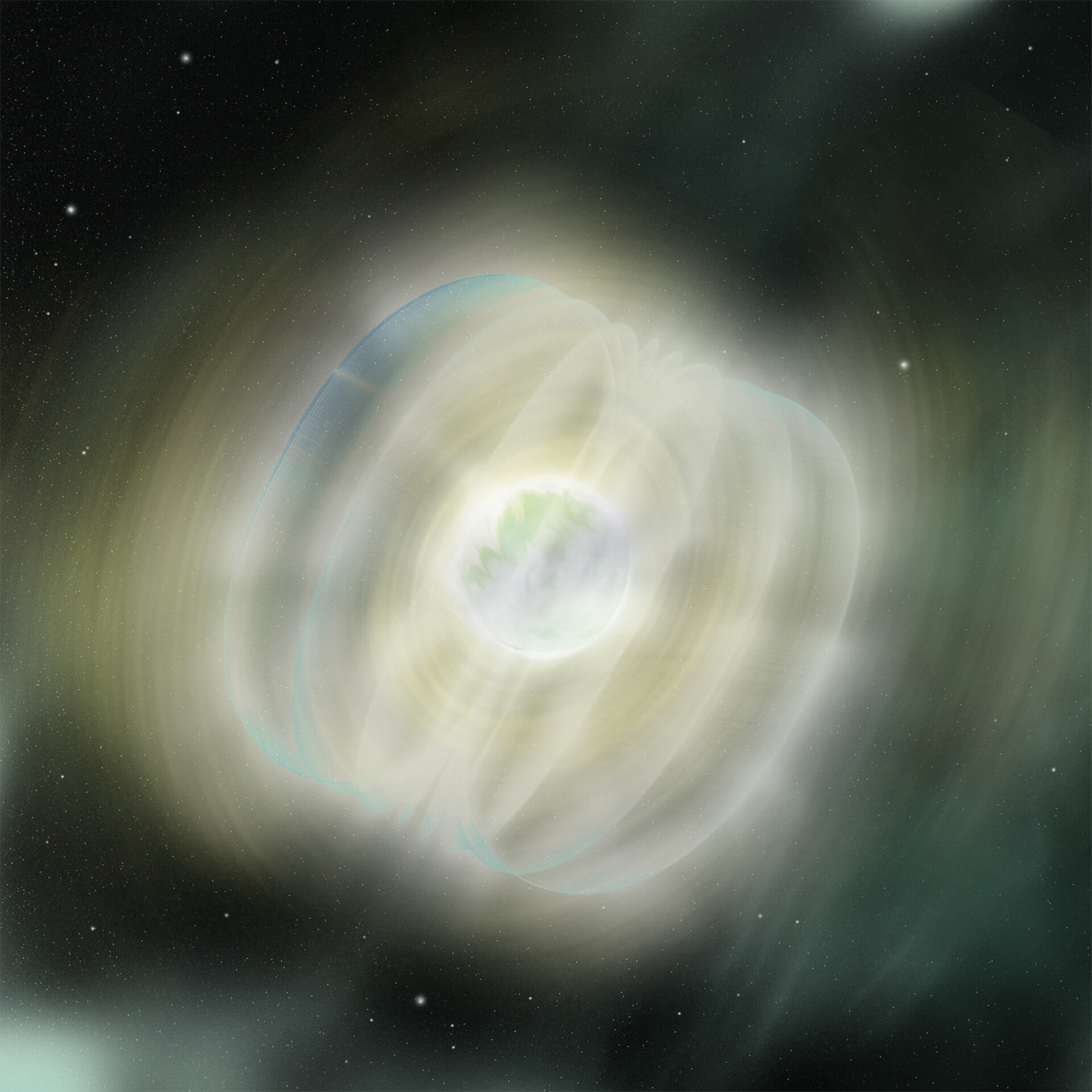
Artist’s impression of a magnetar
Magnetars are neutron stars with extremely powerful magnetic fields. They are extremely dense objects (the size of mountains but weighing as much as the sun), with magnetic fields hundreds of trillions of times more powerful than the Earth’s. The decay of these powerful magnetic fields powers the emission of very energetic radiation, usually in the form of X-rays or Gamma Rays
A seismic event accompanied by a powerful burst was observed on one such magnetar, Westerlund 1 in September 2005. Located in a star cluster about 15 000 light-years away in the Ara constellation in the southern hemisphere, the magnetar goes by the unwieldy official name CXOU J164710.2-455216.





