

Giotto Whipple shield
Thank you for liking
You have already liked this page, you can only like it once!
By spacecraft standards, the 960-kg Giotto was quite modest in size. Its main body was a short cylinder, 1.85 m in diameter by about 1.1 m in height. It contained three interior platforms: the top platform (30 cm thick), a main platform (40 cm), and an experiment platform (30 cm). Each of these consisted of a disc within the cylinder, on which were mounted various subsystems and science experiments. On top of the cylinder was a tripod which surrounded a 1.5 m diameter high-gain dish antenna, which gave the spacecraft a total height of 2.85 m. The main rocket motor was positioned in the centre of the cylinder with the nozzle protruding from the bottom.
The most difficult problem to overcome was how to ensure that Giotto survived long enough to snap its close-up pictures of the comet nucleus when the spacecraft and the comet were heading towards each other at a combined speed of 245 000 km/hour (equivalent to crossing the Atlantic Ocean in 11 minutes!). At this speed, a 0.1-gram dust particle would be able to penetrate 8 cm of solid aluminium. Since it was out of the question to equip Giotto with a 600-kg aluminium shield, engineers turned to a more subtle, 'sandwich' design first proposed by American astronomer Fred Whipple back in 1947 − long before the beginning of the Space Age.
The spacecraft's dust shield consisted of two protective sheets, 23 cm apart. At the front was a sheet of aluminium (1 mm thick), which would vapourise all but the largest of the incoming dust particles. A 12-mm thick sheet of Kevlar at the rear would absorb any debris that pierced the front barrier. Together they could withstand impacts from particles up to 1 gram in mass and travelling 50 times faster than a bullet.
-
CREDIT
ESA -
LICENCE
CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO or ESA Standard Licence
(content can be used under either licence)

Cutaway of the Giotto spacecraft.

ATV shielding after impact test

Giotto spacecraft cutaway
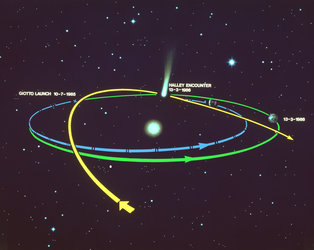
Giotto approaching the nucleus of Halley's Comet

