Applications
Global methane
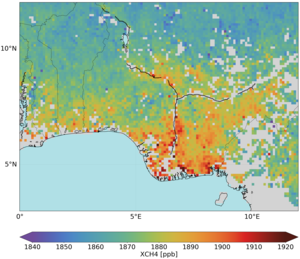
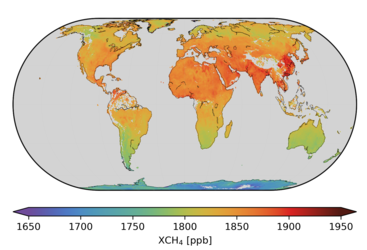
Global distributions of atmospheric methane as retrieved from the Sciamachy instrument on Envisat covering 2003–04 (top) and the TANSO instrument on Japan’s GOSAT from 2010–11 (bottom). High values (yellow to red) correspond to major source regions such as China (e.g., emissions from rice cultivation), Siberia (emissions from wetlands) and parts of the US (e.g., emissions from gas and coal mining, wetlands). During 2010–11 (bottom) the average global methane is approximately 30 parts per billion higher than in 2003–04 (top). Note: the colour scale changes between the two images.