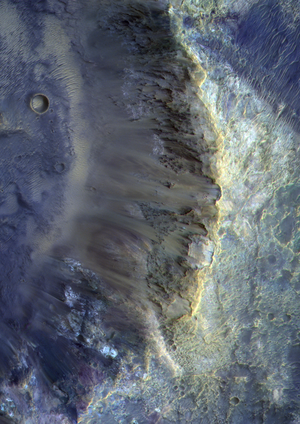
Swirling deposits in a giant impact basin
This mesmerizing image of swirling deposits on Mars was taken by the CaSSIS camera on the ESA-Roscosmos ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter on 9 May 2021.
The swirling and looping texture is typical of the deposits on the floor of the Hellas impact basin in the southern hemisphere of Mars. At 2300 km in diameter and 7 km deep, Hellas is one of the largest identified impact craters both on Mars and within the Solar System.
The terrain imaged in this scene, centred at 52°42'E/39°38'S, is at one of the lowest points of Mars.
The swirling nature of the landscape evokes a feeling of flow. The exact reason for its origin is a puzzle however, and could be attributed to one of many different processes: salt tectonism, or viscous deformation of ice and sediments, for example.
TGO arrived at Mars in 2016 and began its full science mission in 2018. The spacecraft is not only returning spectacular images, but also providing the best ever inventory of the planet’s atmospheric gases, and mapping the planet’s surface for water-rich locations. It will also provide data relay services for the second ExoMars mission comprising the Rosalind Franklin rover and Kazachok platform, when it arrives on Mars in 2023.