Science & Exploration
What's in between stars
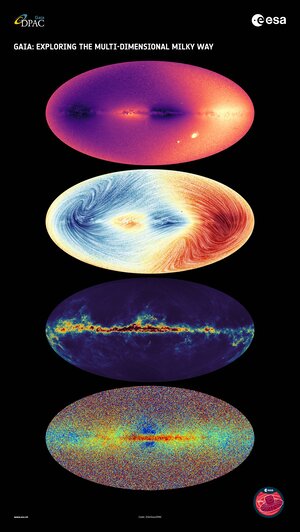
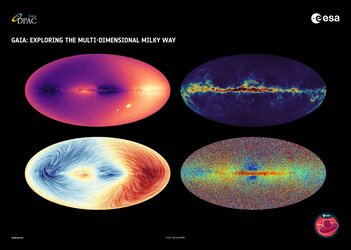
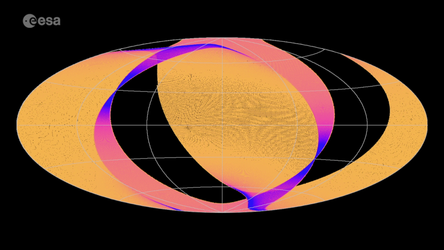
ESA's Gaia mission not only maps the stars in our galaxy, but also what is in between the stars. This is called the interstellar medium, consisting mostly of dust and gas.
Some of the starlight is blocked by dust along the path from the stars to us, which can be measured by Gaia. This allows for a dust map to be created. By studying the dust and gas in between stars, and what they are made of, Gaia helps to understand where and how stars form.