Agency
3D printing skin
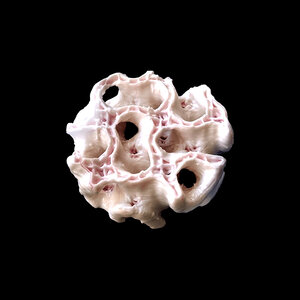
3D printing human tissue could help keep astronauts healthy all the way to Mars. An ESA project has produced its first bioprinted skin and bone samples. This sped-up clip shows the bioprinting of human skin cells using human blood plasma as a nutrient-rich ‘bio-ink’. Plant- and algae-sourced methylcellullose and alginate have been added to increase the viscosity of this bio-ink, to make it suitable for use in low gravity conditions.