Agency
Inside a young star’s accretion disc
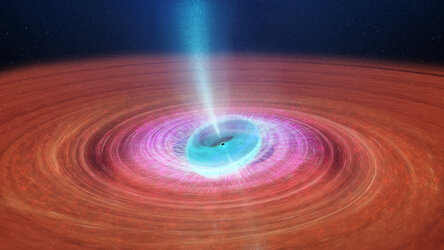
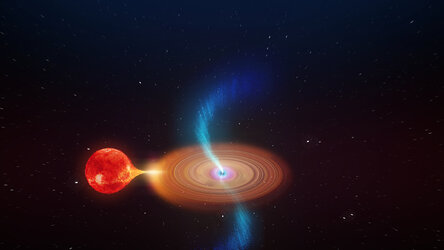
Artist impression of what might be happening behind the thick dust disc surrounding the young Sun-like star V1647 Ori. X-ray observations by ESA’s XMM-Newton, NASA’s Chandra and Japan’s Suzaku space observatories have probed the interior of the dust disc to find a rapidly-rotating star spinning with a period of one day. At 80% the mass of our Sun and with a diameter approximately four times larger, spinning at this rate nears break-up speed for a star of this size. The data also suggest that matter is accreting onto the stellar surface in two pancake-shaped hotspots located on opposite sides of the star, in which the matter heats up and the high temperature plasma is confined.