Satellite constellation
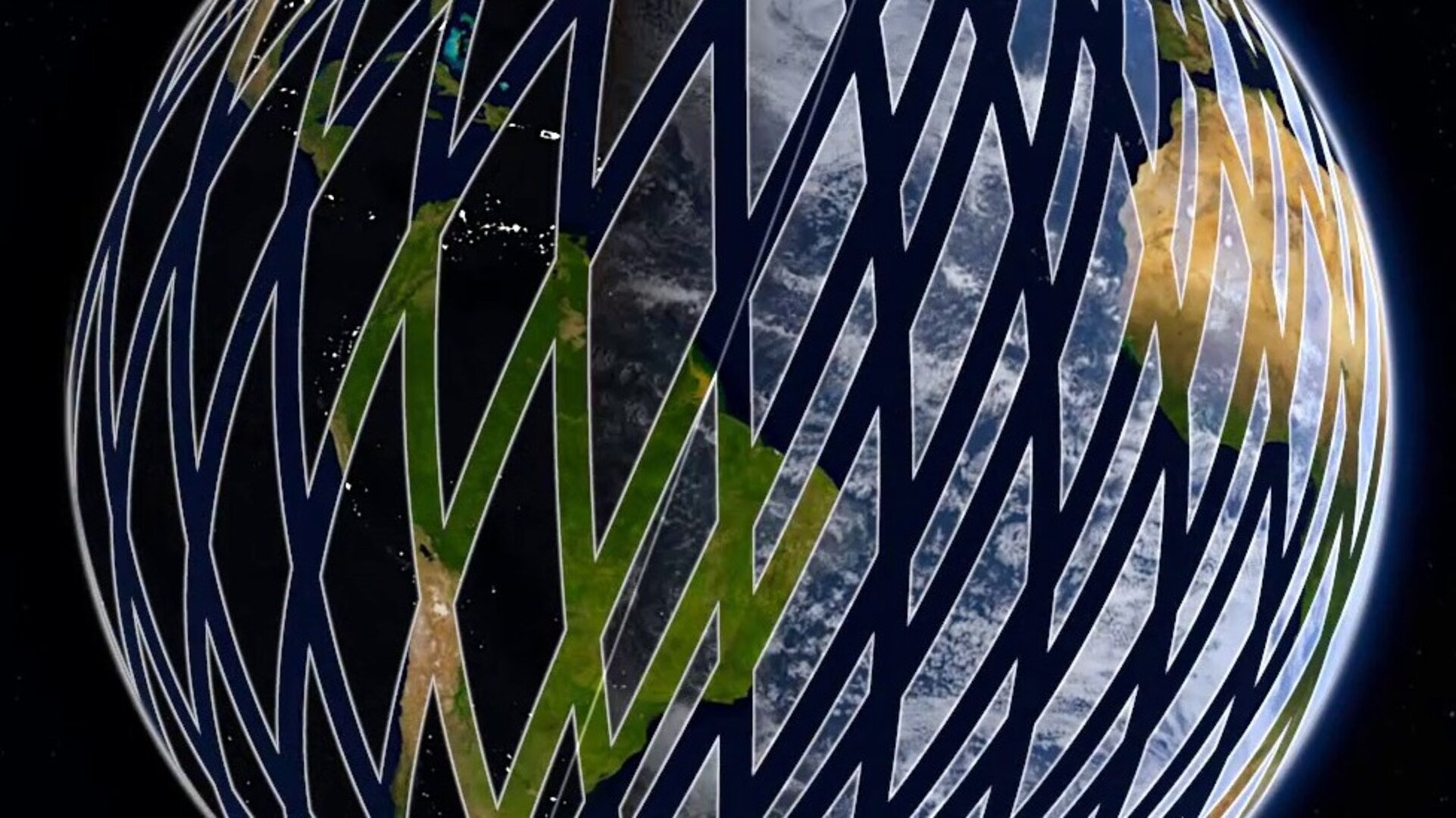
The Sentinel-2 mission is based on a constellation of two satellites, both orbiting Earth at an altitude of 786 km but 180° apart. This configuration optimises coverage and global revisit times.
As a constellation, the same spot over the equator is revisited every five days, and this is even faster at higher latitudes.
Since the US Landsat-8 satellite offers similar imagery and thanks to the cooperation between ESA and NASA, the aim is to reduce this to an average revisit time of just three days over the equator and generate comparable data products.

Designed and built by a consortium of around 60 companies led by Airbus Defence and Space, Sentinel-2 is a prime example of Europe’s technological excellence. The development of the mission has been supported by the French space agency CNES to provide expertise in image processing and calibration, and by the German Aerospace Center DLR which provides the optical communication payloads, developed by Tesat Spacecom GmbH.
In addition to the routine transmission of data to a number of ground stations for rapid dissemination, the optical communications payload transmits data via laser to satellites in geostationary orbit carrying the European Data Relay System (EDRS) and improves the amount and speed of data delivery to the users.
Each satellite, weighing 1140 kg (including fuel) has been designed for a minimum lifetime of seven years, but is expected to last much longer.














 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland