Introducing the Sentinel-4 mission
Air pollution is a global health problem and is also closely linked to the causes of climate change. Air pollutants include trace gases and particles that originate from burning fuel in homes, traffic and industrial facilities. Blown by the wind, desert dust, emissions from wildfires, as well as emissions from volcanoes cause episodes of air pollution.
Trace gases make up less than 0.1 per cent of Earth’s atmosphere but, together with particulate matter such as dust, they can cause severe public health problems as well impact ecosystems.
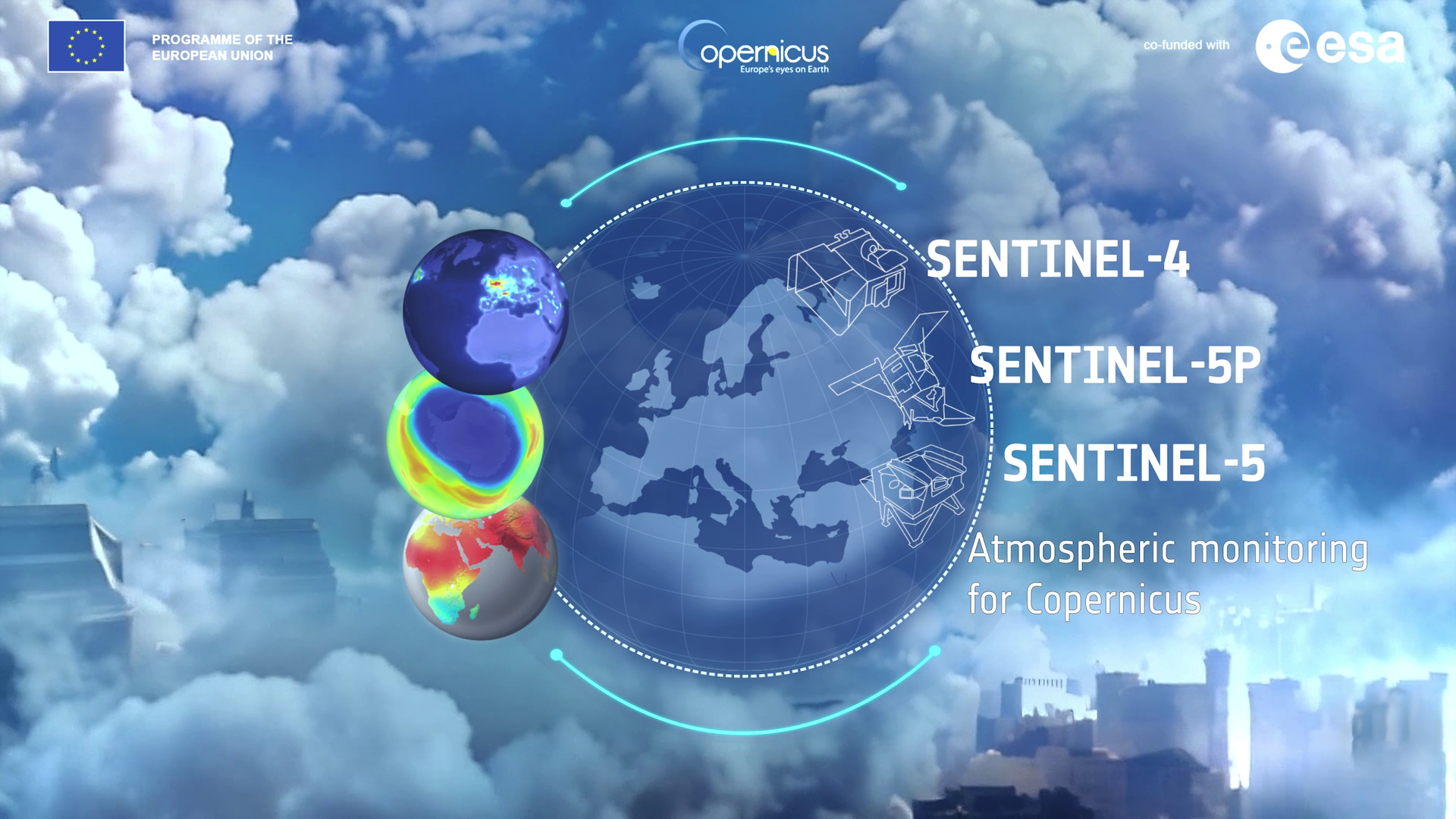
Monitoring air quality from space is an important way to understand the movement and quantity of pollutants and trace gases in the air we breathe – and this is exactly what the Copernicus Sentinel-4 mission does.
With its ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared light spectrometer, or UVN for short, Sentinel-4 delivers high-resolution data on air pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide, ozone, sulphur dioxide and formaldehyde, as well as aerosols.


Access the video
Sentinel-4 provides air quality observations every 60 minutes covering Europe and part of north Africa.
Data from Sentinel-4 along with computer models are used by the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service to provide operational air-quality forecasts, issue health warnings, and to help governments and decision-makers develop appropriate mitigation strategies.
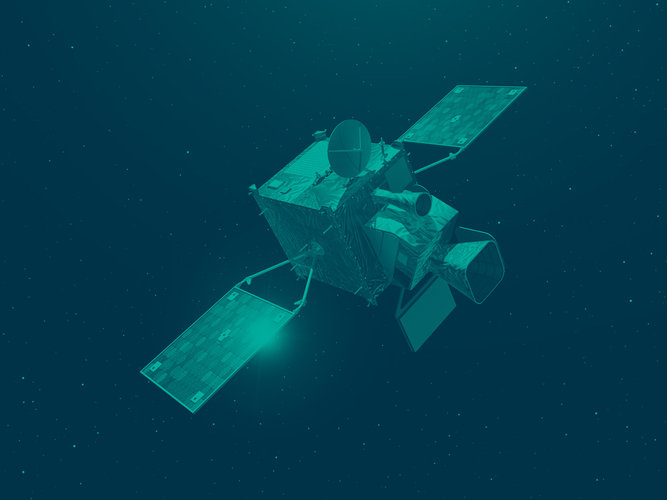
Sentinel-4 is a passenger on the Meteosat Third Generation Sounder (MTG-S) satellites.

There will be two Sentinel-4 missions: one on the first MTG-S, MTG-S1, and the later one on the second, MTG-S2.
The MTG-S1 satellite was launched into geostationary orbit on 1 July 2025. Its position in space means that it is able to maintain a constant position relative to Earth’s surface – at a distance of 36 000 km above the equator. This enables Sentinel-4 to keep a permanent eye on the atmosphere over Europe and north Africa and to scan Earth every 60 minutes.
Sentinel-4 and Sentinel-5 form a constellation of satellite sensors and are complementary in that Sentinel-4 provides hourly observations over Europe with a focus on the fast variations of air pollutants, while Sentinel-5 provides daily global observations of a wider range of atmospheric components relevant to air quality climate and the ozone layer.
Sentinel-4 is also the European contribution to the global constellation of Geostationary Air Quality sensors. The Korean sensor GEMS observes air pollution over Asia, the NASA sensor TEMPO measures air pollution over North America. Together, the three geostationary sensors provide hourly observations covering the key pollution areas in the northern hemisphere.

Access the video
Sentinel-4 benefits from:
- The Infrared Spectrometer on the MTG-S satellites designed, primarily, to observe atmospheric humidity and temperature, but is also sensitive to a number of trace gases observed by Sentinel-4.
- The Flexible Combined Imager instrument on the Meteosat Third Generation Imaging (MTG-I) satellites provides cloud and aerosol information.
- The Lightning Imager instrument on MTG-I detects lightning events, which can be used to estimate nitrogen dioxide production due to lightning.
Cloud observations from the Flexible Combined Imager are used to enhance the Sentinel-4 cloud product. The full synergy achievable by combining observations will be exploited in the future.
The Sentinel-4 mission is the result of close cooperation between ESA, the European Commission, Eumetsat, industry, service providers and data users. Designed and built by ESA through a consortium of companies led by Airbus Defence and Space, the mission is part of Copernicus –the Earth observation component of the European Union’s Space programme.
As with the MTG satellites, Sentinel-4 is operated by Eumetsat. Data processing and distribution are also performed by Eumetsat.














 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland

































