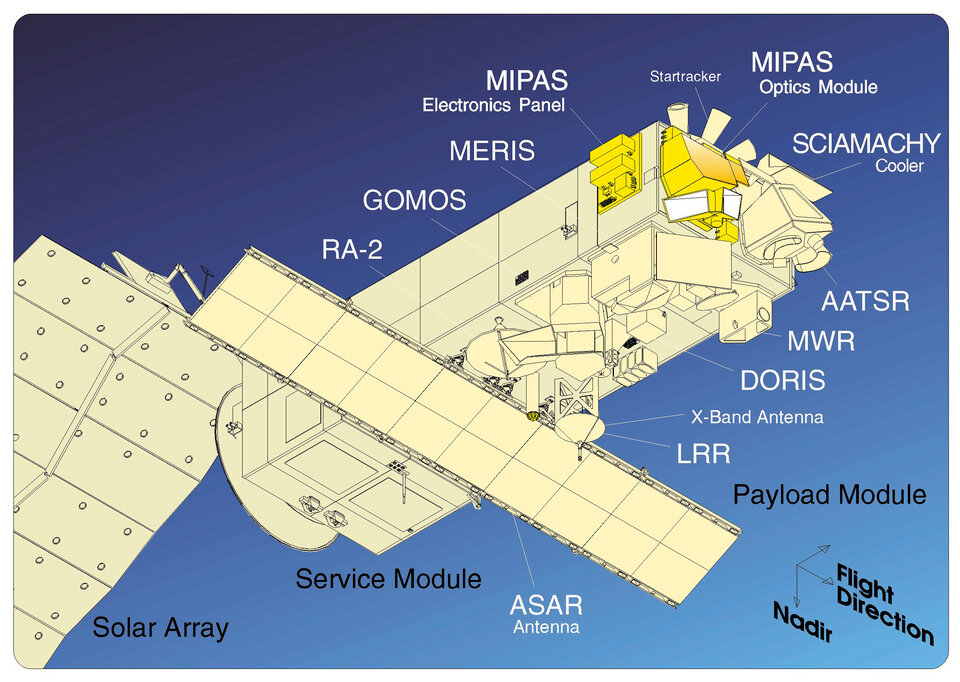
Envisat instruments
Envisat had 10 instruments to provide continuous observation and monitoring of Earth's land, atmosphere, oceans and ice caps:
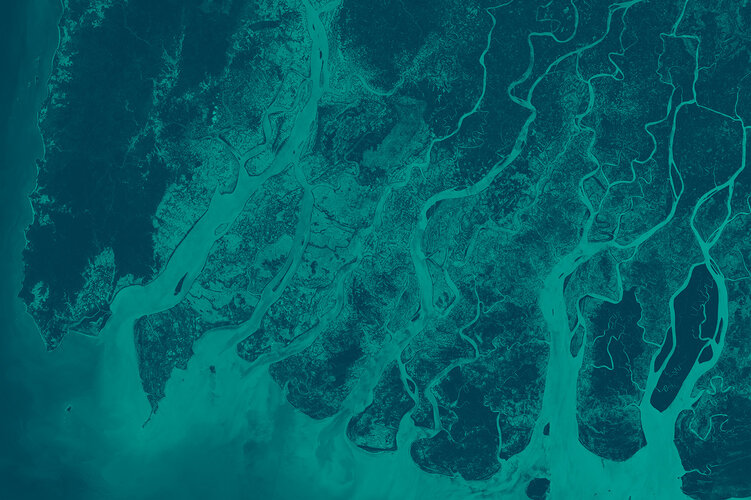
- ASAR (Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar): the largest single instrument on board. Operating in the C-band, it ensured continuity of data after ERS-2. The radar featured enhanced capability in terms of coverage, range of incidence angles, polarisation and modes of operation. The improvements allowed radar beam elevation steerage and the selection of different swaths, 100 or 400 km wide.
- MERIS (Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer): an imaging spectrometer that measured the solar radiation reflected by Earth at a ground spatial resolution of 300 m, with 15 spectral bands in visible and near infra-red and programmable in width and position. MERIS allowed global coverage of Earth every three days. The primary mission of MERIS was the measurement of sea colour in oceans and coastal areas.
- AATSR (Advanced Along Track Scanning Radiometer): an infrared radiometer providing high resolution and high accuracy temperature information, for applications such as sea surface temperature or fire observation.

- SCIAMACHY: an imaging spectrometer whose primary mission objective was to perform global measurements of trace gases in the troposphere and stratosphere.
- MIPAS (Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric Sounding): an instrument that looked further into the infrared part of the spectrum and complemented SCIAMACHY. It provided information on additional trace gases and atmospheric temperatures.
- GOMOS (Global Ozone Monitoring by Occultation of Stars): dedicated to atmospheric monitoring, GOMOS was a medium resolution spectrometer that primarily measured stratospheric ozone.
- DORIS (Doppler Orbitography and Radio-positioning Integrated by Satellite): a microwave tracking system that was used to determine the precise location of the Envisat satellite.
- RA-2 (Radar Altimeter): an instrument for determining the two-way delay of the radar echo from Earth's surface to a very high precision - less than a nanosecond. It also measured the power and shape of the reflected radar pulses.
- MWR: a microwave radiometer that measured integrated atmospheric water vapour column and cloud liquid water content, as correction terms for the radar altimeter signal. In addition, MWR measurement data are useful for the determination of surface emissivity and soil moisture over land, for surface energy budget investigations to support atmospheric studies, and for ice characterisation.
- LRR (Laser Retro Reflector): a passive device which was used as a reflector by ground-based SLR stations using high-power pulsed lasers. In the case of Envisat, tracking using the LRR was mainly accomplished by the International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS).















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland