Galileo in place for launch: then there were four
Two more Galileo satellites have reached Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana, joining the first pair of navigation satellites and the Ariane 5 rocket due to haul the quartet to orbit this December.
Galileos 21 and 22 left Luxembourg Airport on a Boeing 747 cargo jet on the morning of 17 October, arriving at Cayenne – Félix Eboué Airport in French Guiana on the same day.
Resting within distinctive white air-conditioned containers, the satellites were driven to the cleanroom environment of the preparation building within the space centre.
Waiting for them there were Galileos 19 and 20, which arrived in September.

The four satellites will be launched together in mid-December by a customised Ariane 5, the elements of which reached French Guiana last month by sea.
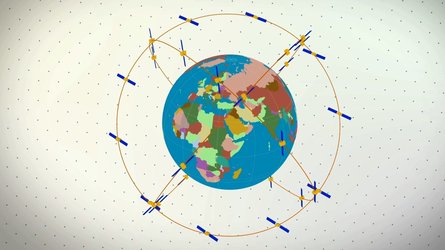
Galileo is Europe’s own satellite navigation system, providing an array of positioning, navigation and timing services to Europe and the world.
A further eight Galileo ‘Batch 3’ satellites were ordered last June, to supplement the 26 built so far.

With 18 satellites now in orbit, Galileo began initial services on 15 December 2016, the first step towards full operations.
Further launches will continue to build the constellation, which will gradually improve performance and availability worldwide.

About Galileo
Galileo is the EU’s own global satellite navigation system, consisting of both the satellites in space and their associated ground infrastructure.
The definition, development and in-orbit validation phases were carried out by ESA, and co-funded by ESA and the European Commission. This phase created a mini constellation of four satellites and a reduced ground segment set up to validate the overall concept, ahead of further deployment.
Success led to the current Full Operational Capability phase, fully funded by the EU and managed by the Commission. The Commission and ESA have a delegation agreement by which ESA acts as design and procurement agent on behalf of the Commission.















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland