Science & Exploration
Orion of the future
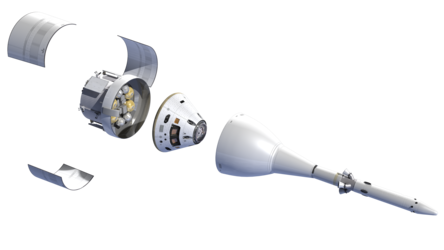
NASA’s Orion spacecraft, seen during Exploration Mission 1 in the late 2010s, will carry astronauts further into space than ever before using the European Service Module, developed on the heritage of ESA’s Automated Transfer Vehicles (ATV).
ATV’s distinctive four-wing solar array is recognisable in this concept. The ATV-derived service module, sitting directly below Orion’s crew capsule, will contain the propulsion capability for orbital transfer, attitude control and high-altitude ascent aborts. It will also generate power using solar wings and provide thermal control, water, oxygen and nitrogen for the astronauts until just before their return to Earth, when it will separate from the crew module.