Accept all cookies Accept only essential cookies See our Cookie Notice

About ESA
The European Space Agency (ESA) is Europe’s gateway to space. Its mission is to shape the development of Europe’s space capability and ensure that investment in space continues to deliver benefits to the citizens of Europe and the world.
Highlights
ESA - United space in Europe
This is ESA ESA facts Member States & Cooperating States Funding Director General Top management For Member State Delegations European vision European Space Policy ESA & EU Space Councils Responsibility & Sustainability Annual Report Calendar of meetings Corporate newsEstablishments & sites
ESA Headquarters ESA ESTEC ESA ESOC ESA ESRIN ESA EAC ESA ESAC Europe's Spaceport ESA ESEC ESA ECSAT Brussels Office Washington OfficeWorking with ESA
Business with ESA ESA Commercialisation Gateway Law at ESA Careers Cyber resilience at ESA IT at ESA Newsroom Partnerships Merchandising Licence Education Open Space Innovation Platform Integrity and Reporting Administrative Tribunal Health and SafetyMore about ESA
History ESA Historical Archives Exhibitions Publications Art & Culture ESA Merchandise Kids Diversity ESA Brand CentreLatest
Space in Member States
Find out more about space activities in our 23 Member States, and understand how ESA works together with their national agencies, institutions and organisations.
Science & Exploration
Exploring our Solar System and unlocking the secrets of the Universe
Go to topicAstronauts
Missions
Juice Euclid Webb Solar Orbiter BepiColombo Gaia ExoMars Cheops Exoplanet missions More missionsActivities
International Space Station Orion service module Gateway Concordia Caves & Pangaea BenefitsLatest
Space Safety
Protecting life and infrastructure on Earth and in orbit
Go to topicAsteroids
Asteroids and Planetary Defence Asteroid danger explained Flyeye telescope: asteroid detection Hera mission: asteroid deflection Near-Earth Object Coordination CentreSpace junk
About space debris Space debris by the numbers Space Environment Report In space refuelling, refurbishing and removingSafety from space
Clean Space ecodesign Zero Debris Technologies Space for Earth Supporting Sustainable DevelopmentSpace weather
Space weather and its hazards ESA Vigil: providing solar warning ESA Space Weather Service NetworkLatest
Applications
Using space to benefit citizens and meet future challenges on Earth
Go to topicObserving the Earth
Observing the Earth Future EO Copernicus Meteorology Space for our climate Satellite missionsCommercialisation
ESA Commercialisation Gateway Open Space Innovation Platform Business Incubation ESA Space SolutionsLatest
Enabling & Support
Making space accessible and developing the technologies for the future
Go to topicBuilding missions
Space Engineering and Technology Test centre Laboratories Concurrent Design Facility Preparing for the future Shaping the Future Discovery and Preparation Advanced Concepts TeamSpace transportation
Space Transportation Ariane Vega Space Rider Future space transportation Boost! Europe's Spaceport Launches from Europe's Spaceport from 2012Latest
Annual global ice loss simulated over Oslo
Thank you for liking
You have already liked this page, you can only like it once!
Satellites play a vital role in monitoring the rapid changes taking place in the Arctic. Tracking ice lost from the world’s glaciers, ice sheets and frozen land shows that Earth is losing ice at an accelerating rate.
Using information from ESA’s ERS, Envisat and CryoSat satellites as well as the Copernicus Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 missions, research led by Tom Slater of the University of Leeds, found that the rate at which Earth has lost ice has increased markedly within the past three decades. Currently, more than a trillion tonnes of ice is lost each year.
To put this into perspective, this is equivalent to an ice cube measuring 10x10x10 km over Oslo’s skyline. Putting it another way, the amount of ice loss globally is equivalent to 12 000 times the annual water use of the Norwegian capital.
The sooner Earth’s temperature is stabilised, the more manageable the impacts of ice loss will be.
Continuity in satellite data is the key to predicting future ice losses, and to assist in mitigating the threats posed by sea-level rise, shrinking high mountain glaciers and further climate feedbacks. The Copernicus Expansion missions, CRISTAL, CIMR and ROSE-L have been designed to fill the gaps in current Sentinel capabilities for comprehensive monitoring of changes in the global ice cover.
-
CREDIT
Planetary Visions (credit: ESA/Planetary Visions) -
LICENCE
ESA Standard Licence
-
Closed captions available Captions and subtitles are available (automatically generated by YouTube) - select your language using the YouTube player controls. A non-YouTube version is available using the 'download' button above.
-
Documentary
-
-
-

Sea ice over Oslo
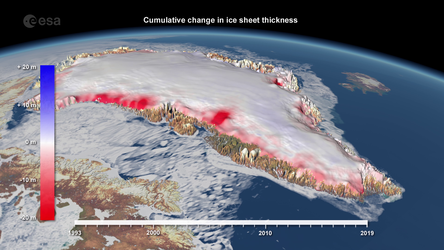
Ice loss from Greenland and Antarctica

Global ice loss

Greenland ice loss















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
























