Compact waveguide orthomode transducer
| 747 - Abstract: |
| Dual-polarization waveguide feed chains are a key sub-system in most radio frequency (RF) satellite payloads as well as reflector based ground antennas. There is a need for compact feed chains without compromising RF performance. The present invention proposes a two-probe orthomode transducer or junction which provides high cross-polarization discrimination (XPD) thanks to an asymmetric common waveguide cross-section. It may be combined with other methods to enhance the feed chain performance while keeping a compact design. ESA is looking for partners who would be interested in getting a license and implementing this patent. |
Description:
Dual-polarization waveguide feed chains are a key sub-system in most radio frequency (RF) satellite payloads as well as reflector based ground antennas. For example, horn antennas are commonly used as part of reflector and array antenna sub-systems in RF satellite payloads because of their high performance and low insertion losses. They are generally fed by orthomode transducers (OMT) or orthomode junctions (OMJ), enabling polarization diversity and/or multiple frequency operation, typically at least transmit (Tx) and receive (Rx) bands.
Four-probe OMT designs were for a long time the preferred approach, as this symmetric design naturally provides high-order modes rejection. A typical approach to achieve high performance is to have the 4-probe OMT closer to the horn operating in the lower frequency band (Tx band for the onboard feed chains). A typical 4-probe design will have a footprint diameter of about 5/6 wavelengths at the highest operating frequency (e.g. 50 to 60 mm at 30 GHz), including the probe filters and combining network (for linear or circular polarization operation).
However, with the advent of high throughput satellites (HTS), requiring hundreds of beams and hence, hundreds of feed chains, the reduction of the footprint of feed chains without compromising performance has become a prime issue.
As mentioned above, the pior art found is characterized by a common waveguide having a cross section with a discrete rotational symmetry of order 4 (e.g. circular, square). This is to provide similar operation for the two orthogonal components of the coupled electric field.

The main key differentiating feature of the present invention with respect to the current solutions is the introduction of some asymmetry in the shape of the common waveguide cross-section. Typical cross section shapes would be ellipses, rhombuses, circles or squares either chamfered or with ridges on one axis, and any combination of those. The two axes of symmetry are rotated with respect to the two orthogonal reference axes, corresponding to the axes of the probes, by an angle of approximately 45 degrees.
A schematic representation of the invention in the case of an elliptical cross section is provided in Figure 1.
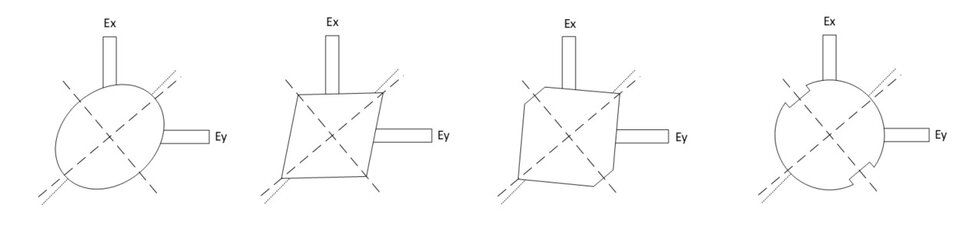
Variations of the invention are illustrated in Figure 2 (the selection being mostly driven by the interconnection with the remaining parts of the antenna feed (e.g. horn, OMT in the other band, etc).
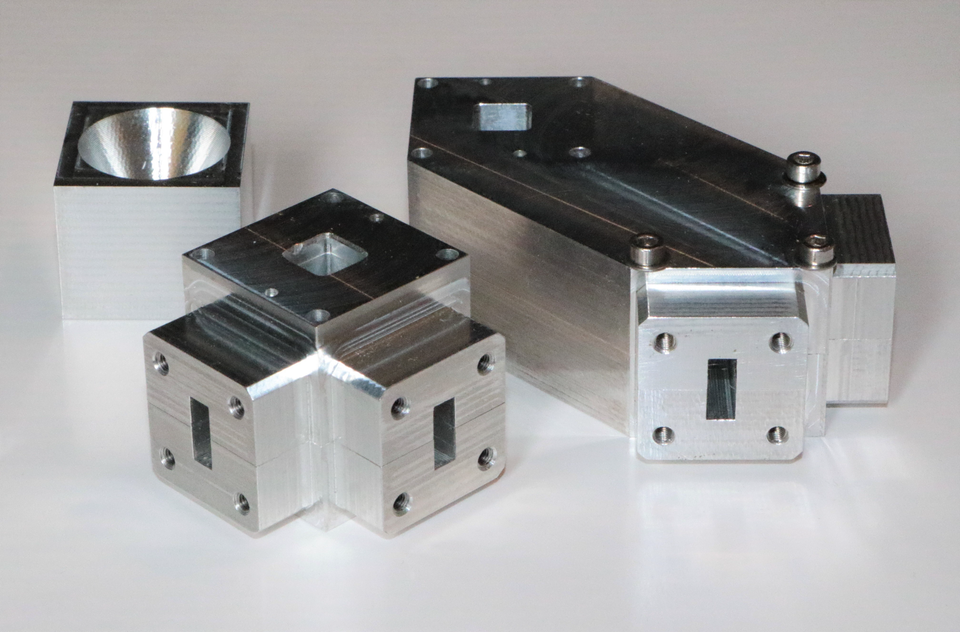

Dual-linear and dual-circular OMT designs have been manufactured and tested in the K-band, with performance in line with predictions. Further details are available upon request.
Innovations and advantages:
- Compact design without compromising RF performance.
- It is complementary to existing solutions and could advantageously be combined with them to enhance further the performance and/or compactness of existing antenna feed products.
- It can be used equally for dual-circular and dual-linear applications.
- It may be manufactured using alternative techniques, such as additive layer manufacturing and diffusion bonding.
- It’s a generic solution; the cross-section shape may be adjusted to match the cross-section of the other components connected to the OMT (e.g. horn antenna, septum polarizer).
Domain of application:
This concept could find applications not only in the satcom field but also in Earth observation or Science missions, as dual-polarization waveguide feeds are a common subsystem in satellite RF payloads.
Outside the space field, this invention could be of interest for terrestrial communication (5G), measurement systems in the millimeter and sub-millimeter wave range (e.g. test facility probes, material characterization test bench).
IP Status
An International patent application (PCT) has been filed.















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland

























