Mars Express science highlights
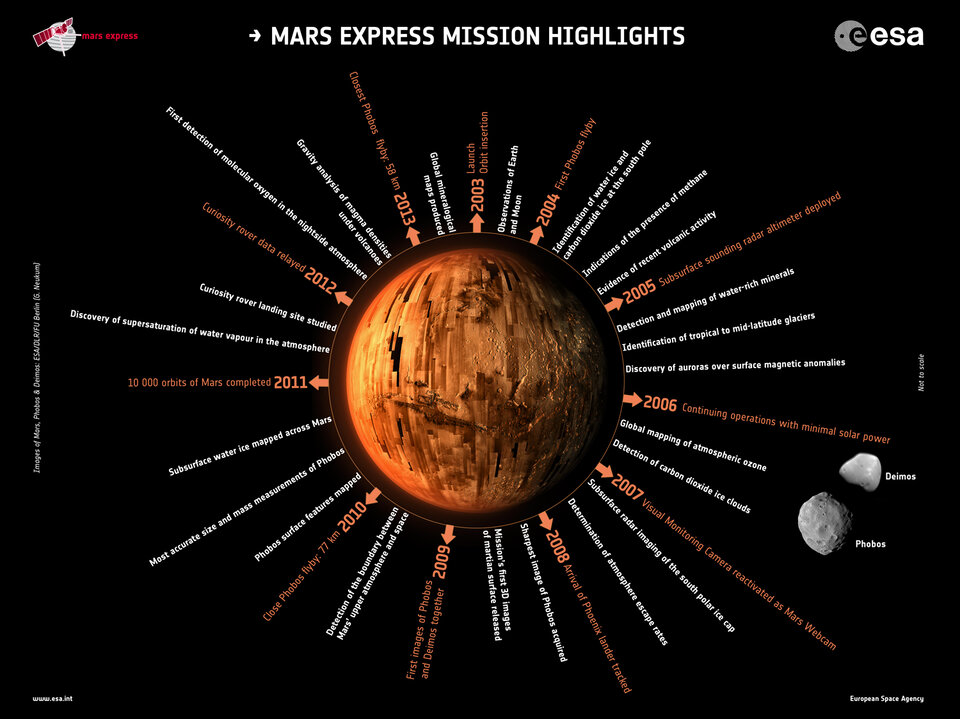
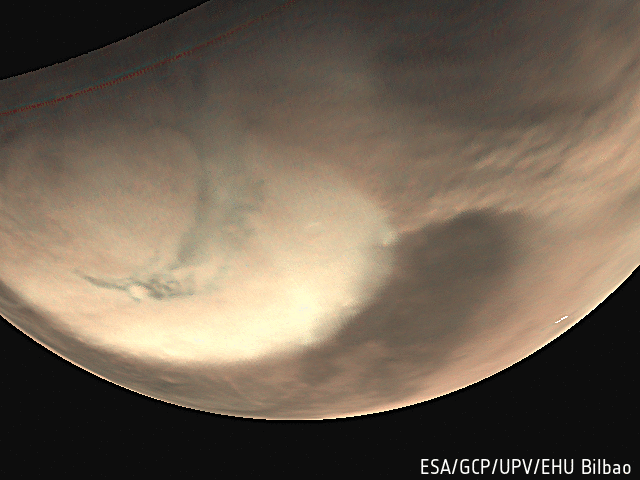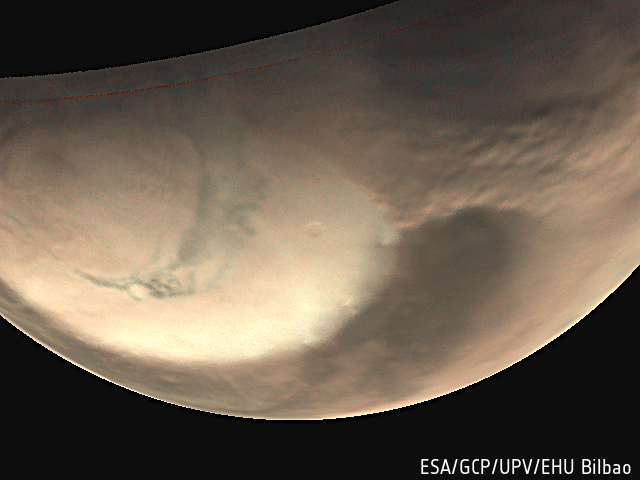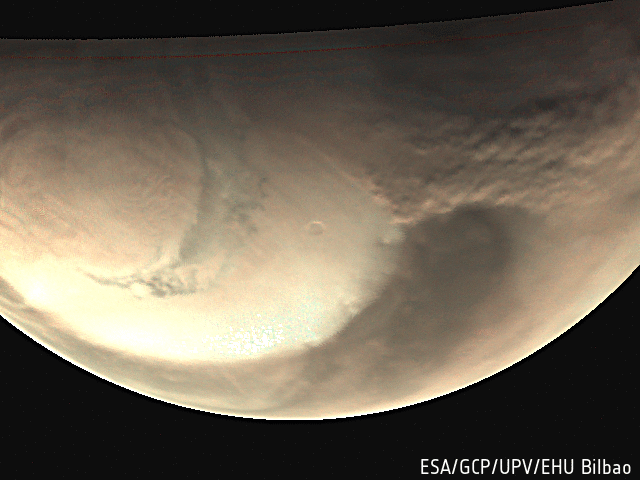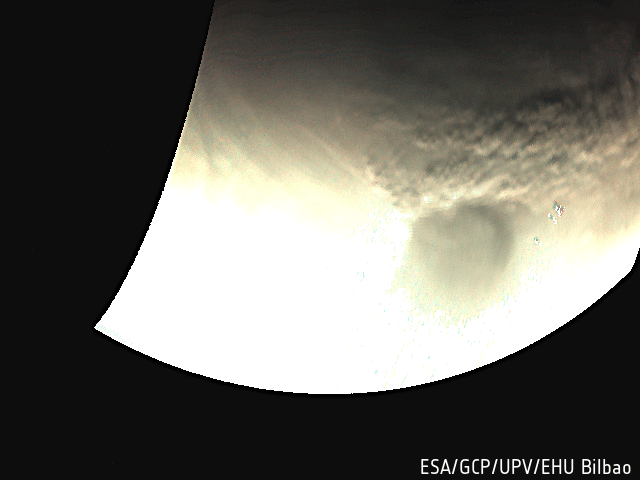
Mars Express has provided an unprecedented breadth and depth of information about Mars, from providing the most complete map of the chemical composition of the atmosphere, to tracing the history of water across the globe.
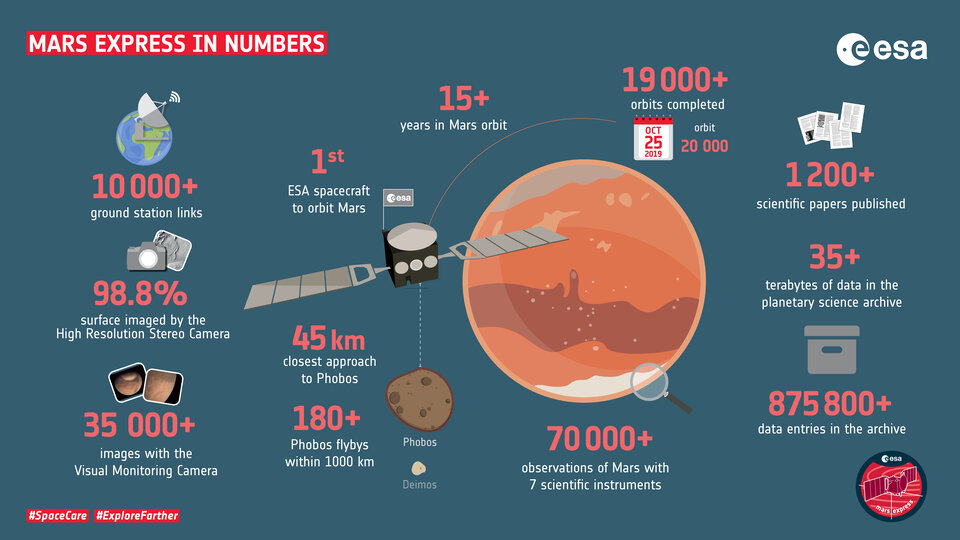
Some of the key results include:
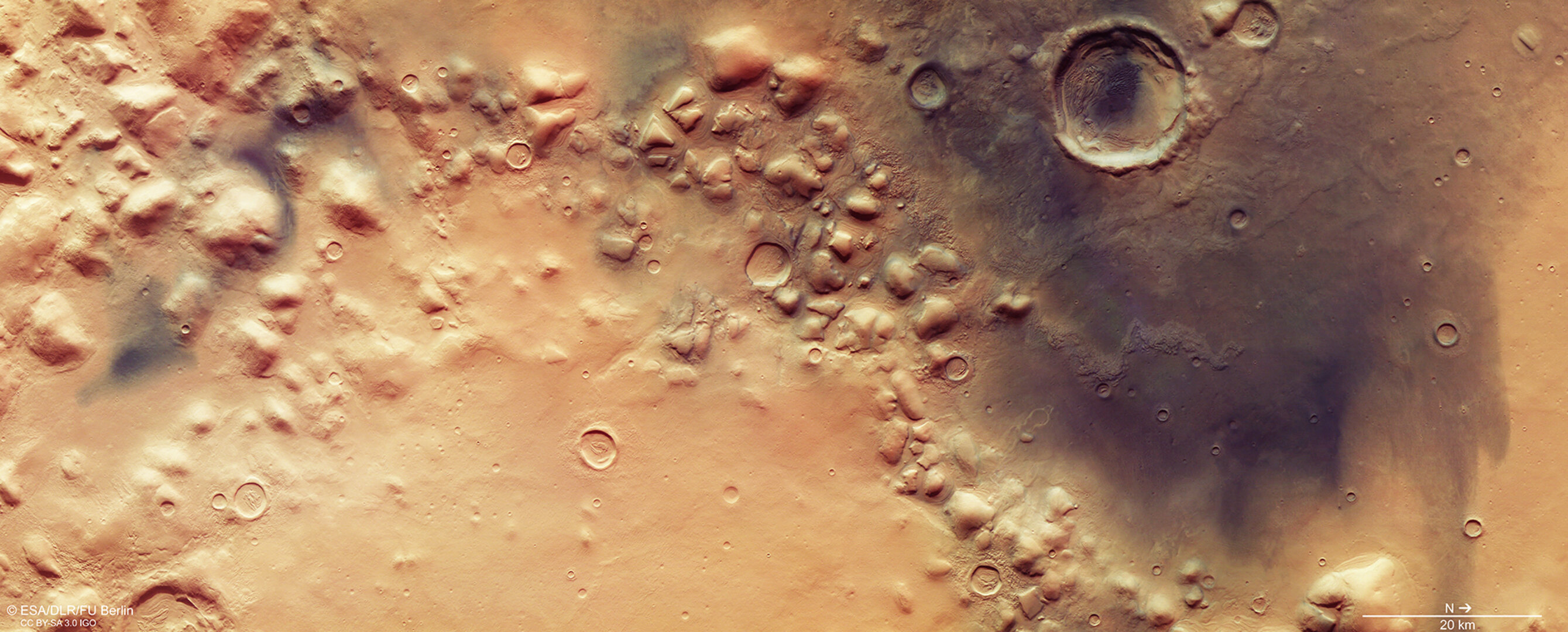
- Producing global maps tracing the planet’s geologic activity, water, volcanism and minerals.
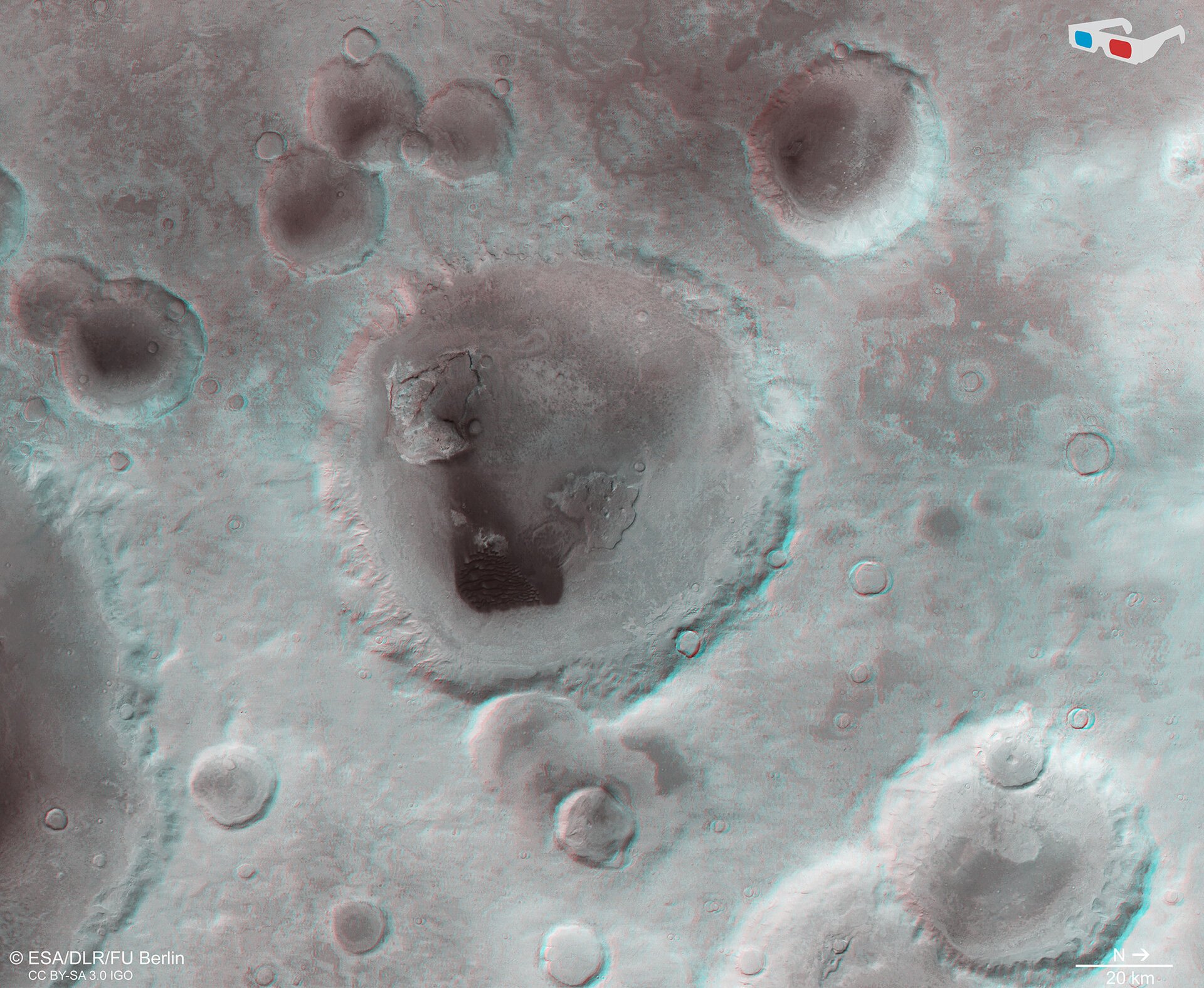
- Providing enough data to construct thousands of 3D images of the surface.
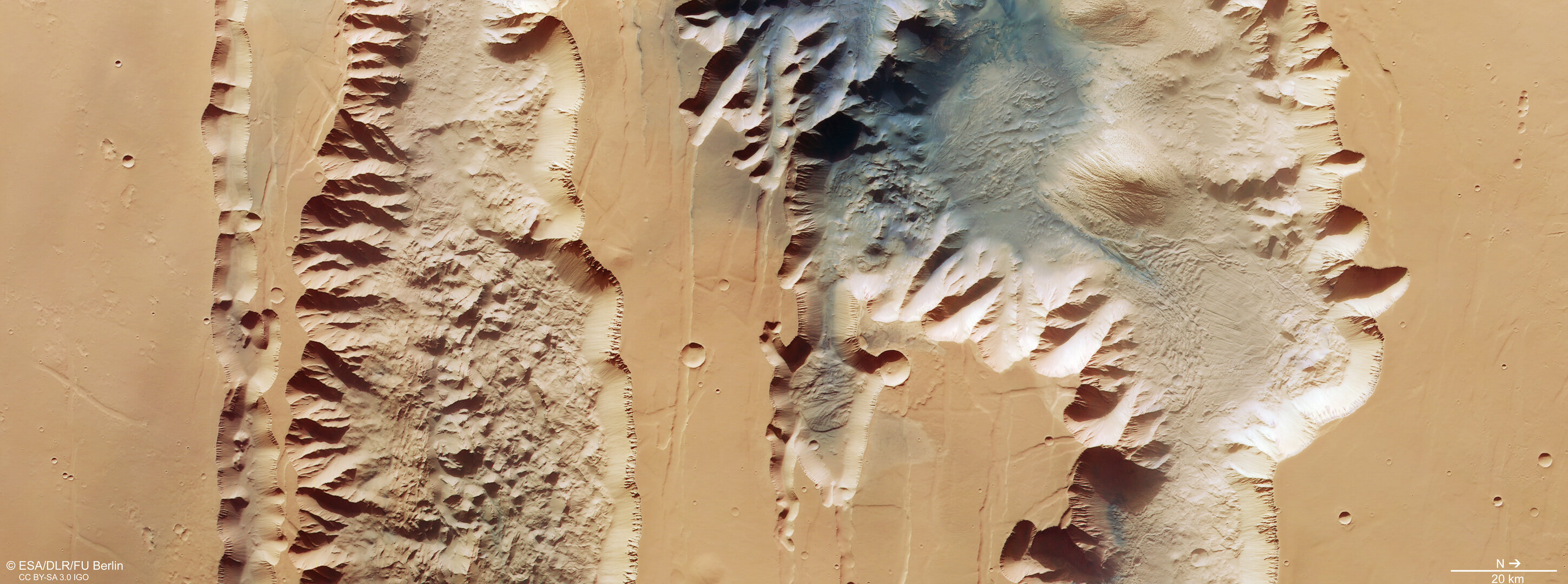
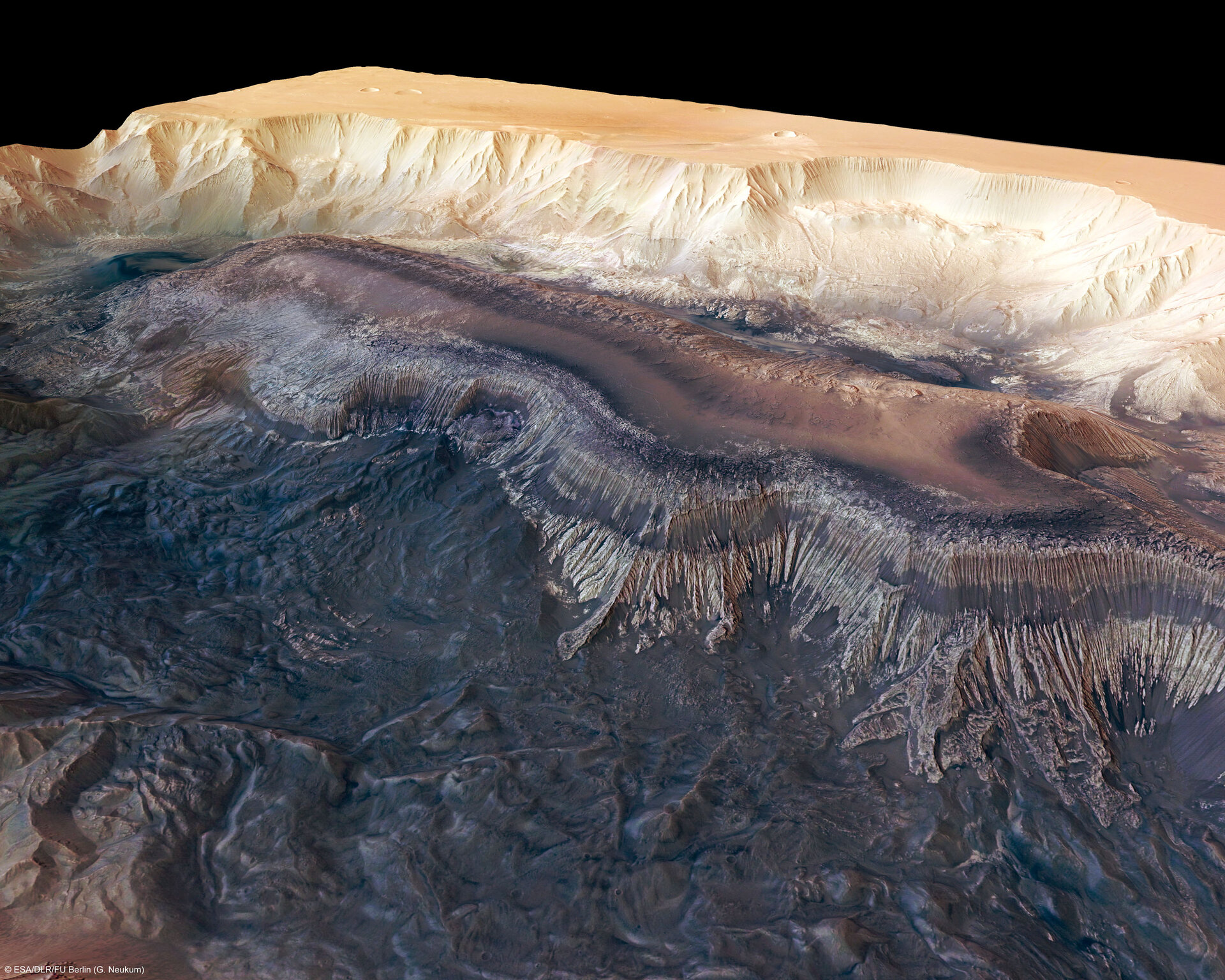
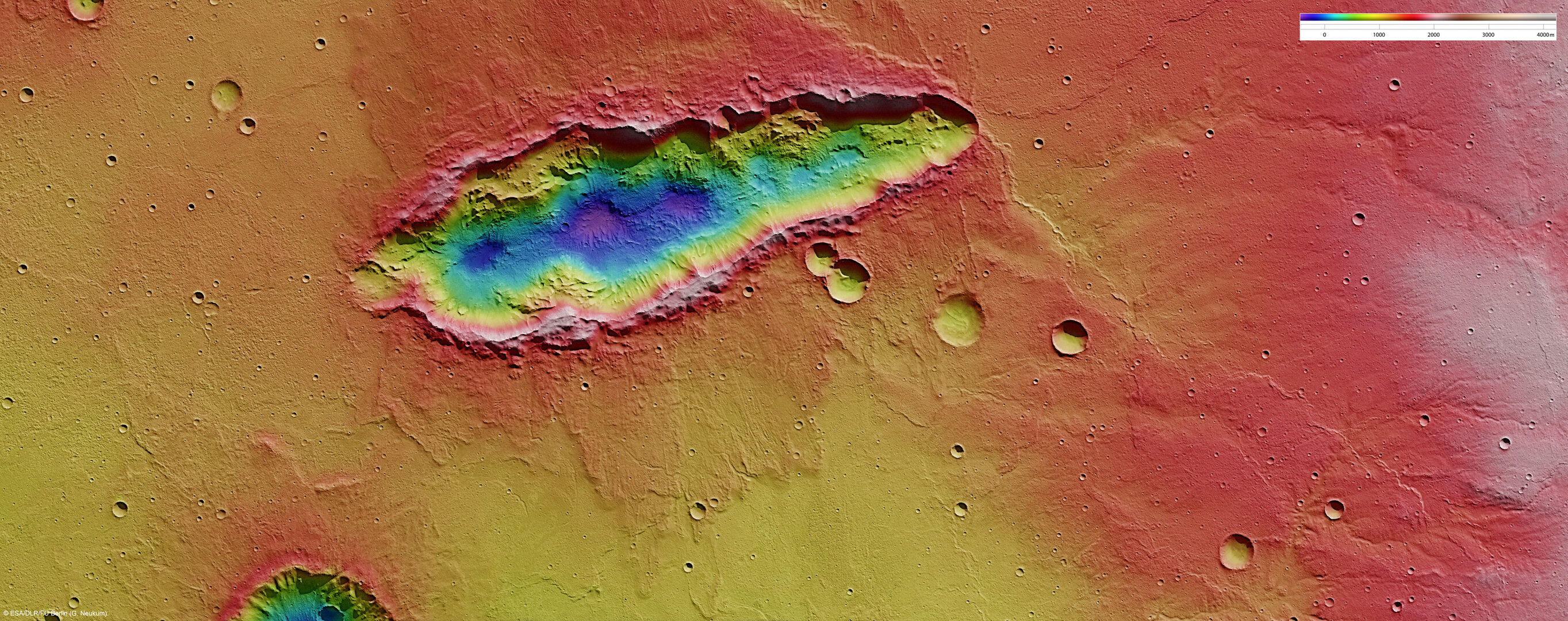
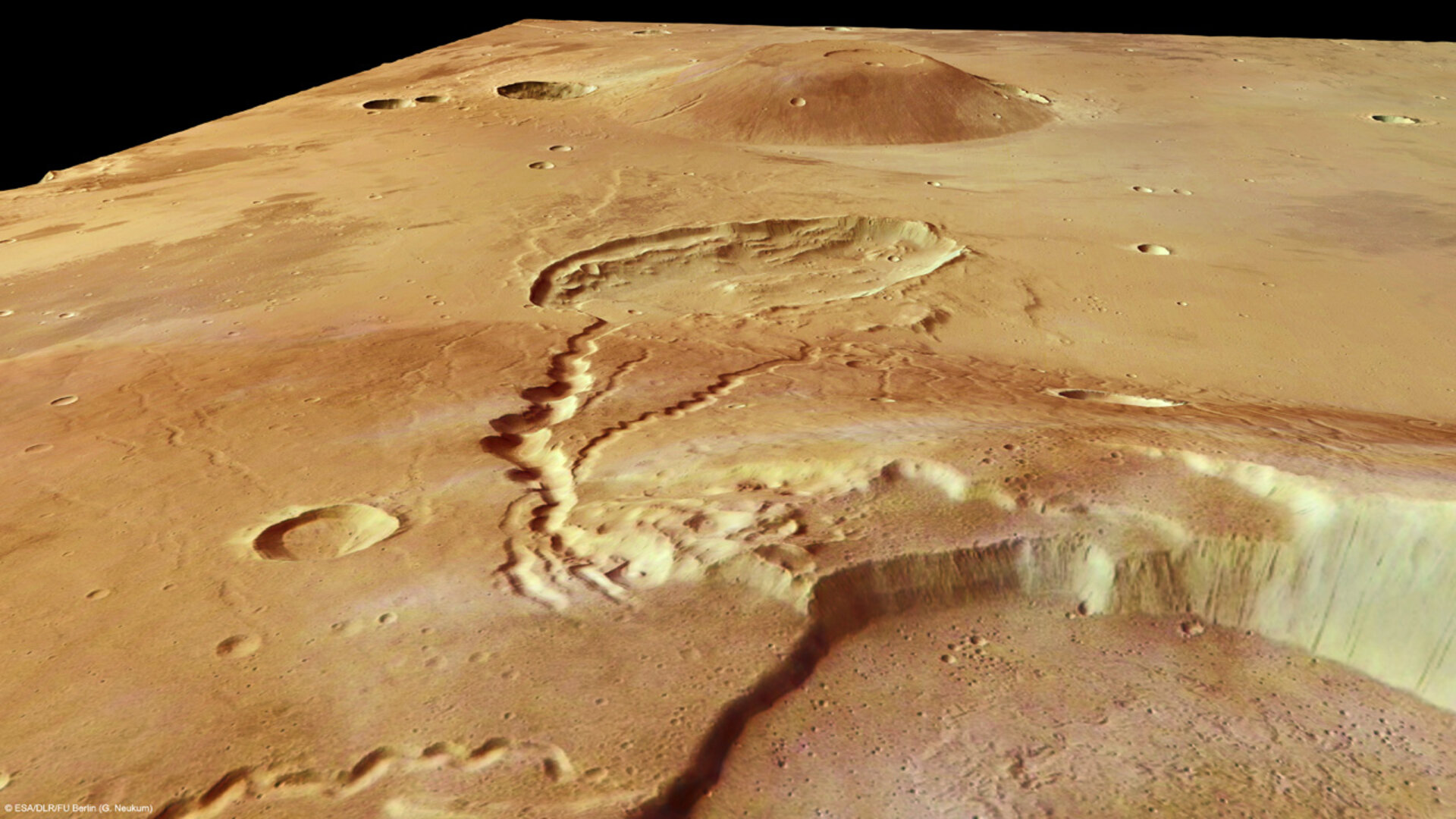
- Studying immense volcanoes, canyons, polar ice caps, and ancient impact craters.
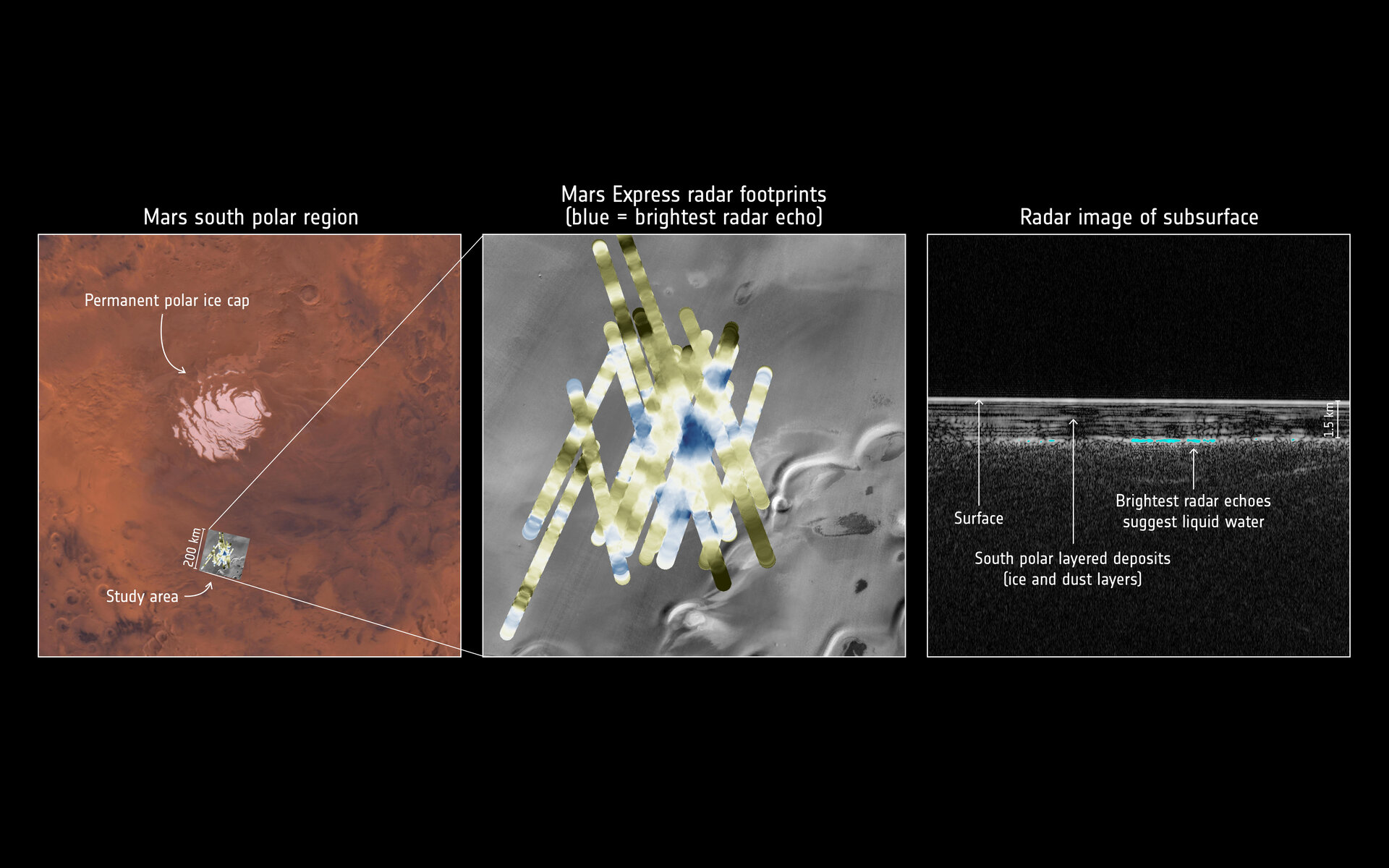
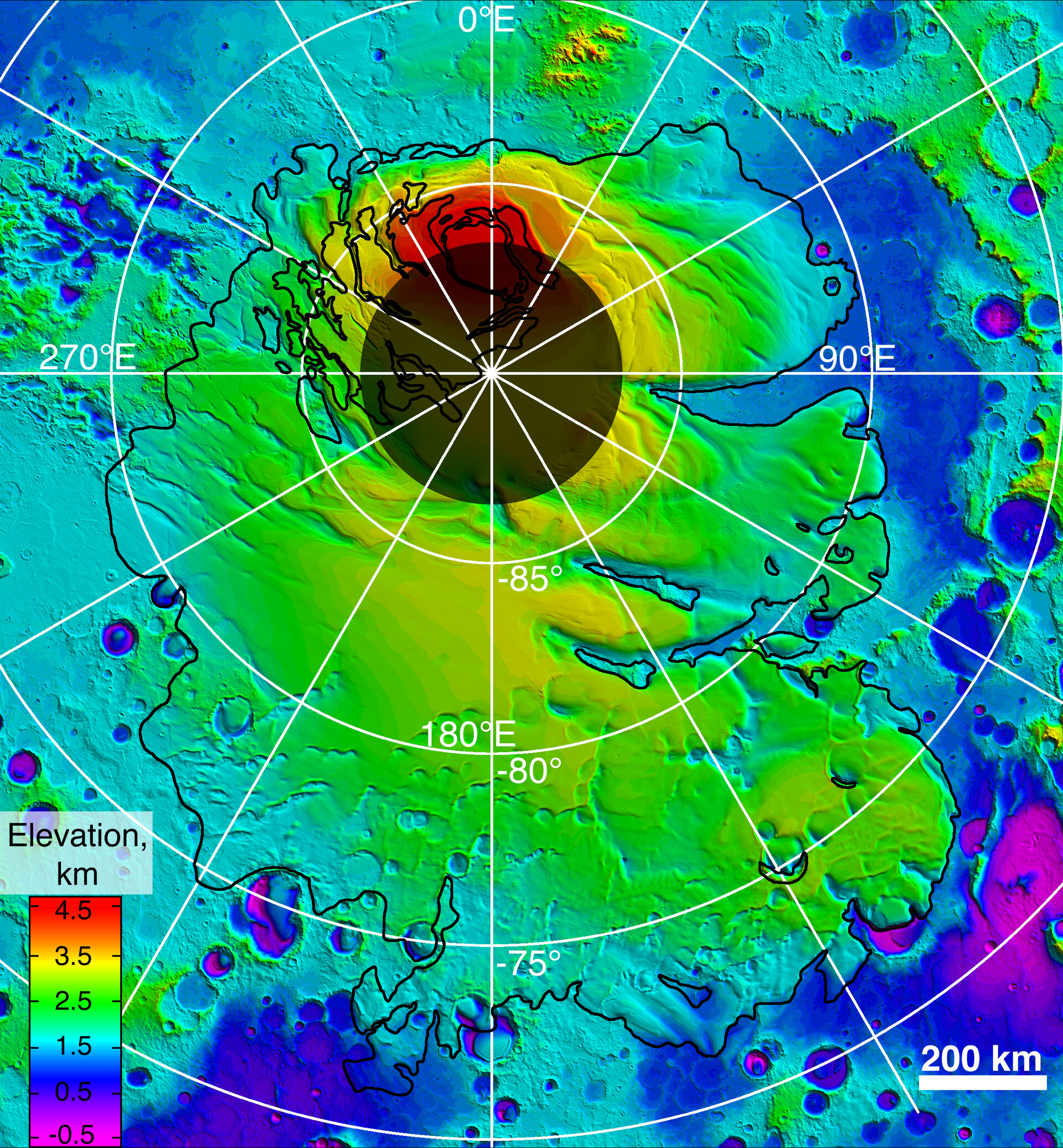
- Probing the sub-surface with radar, detecting subsurface layers of water ice and liquid water hidden under the planet's south pole.
- Explored the martian atmosphere, finding signs of ozone and methane (which on Earth is attributed to active volcanism and biochemical processes), fleeting cloud layers up to 100 km above Mars' surface, and mighty dust storms.
- Witnessing charged particles escaping to space.
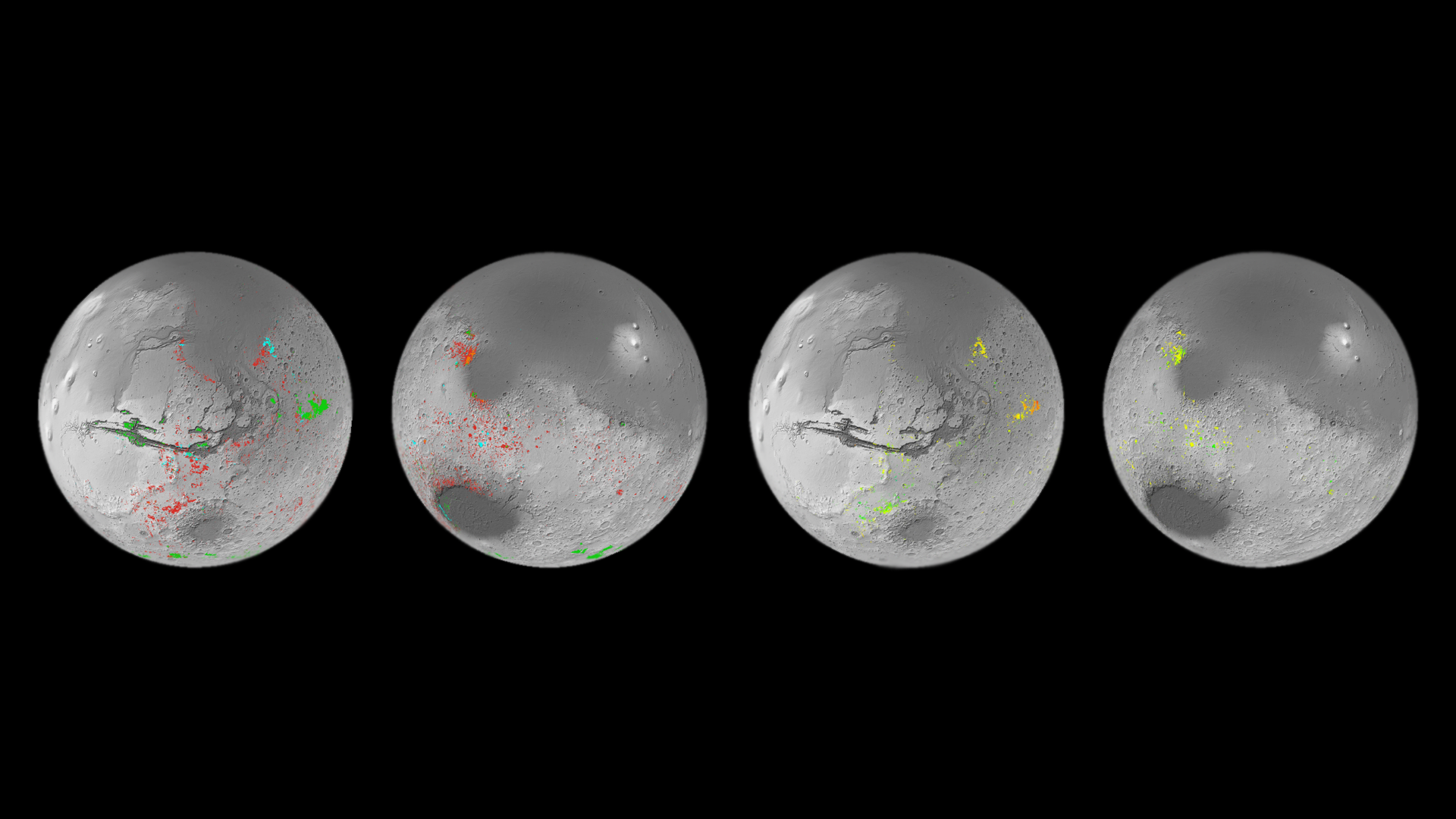
- Finding the first evidence of a planet-wide groundwater system. Five of these ancient interconnected underground lakes may contain minerals crucial to life.
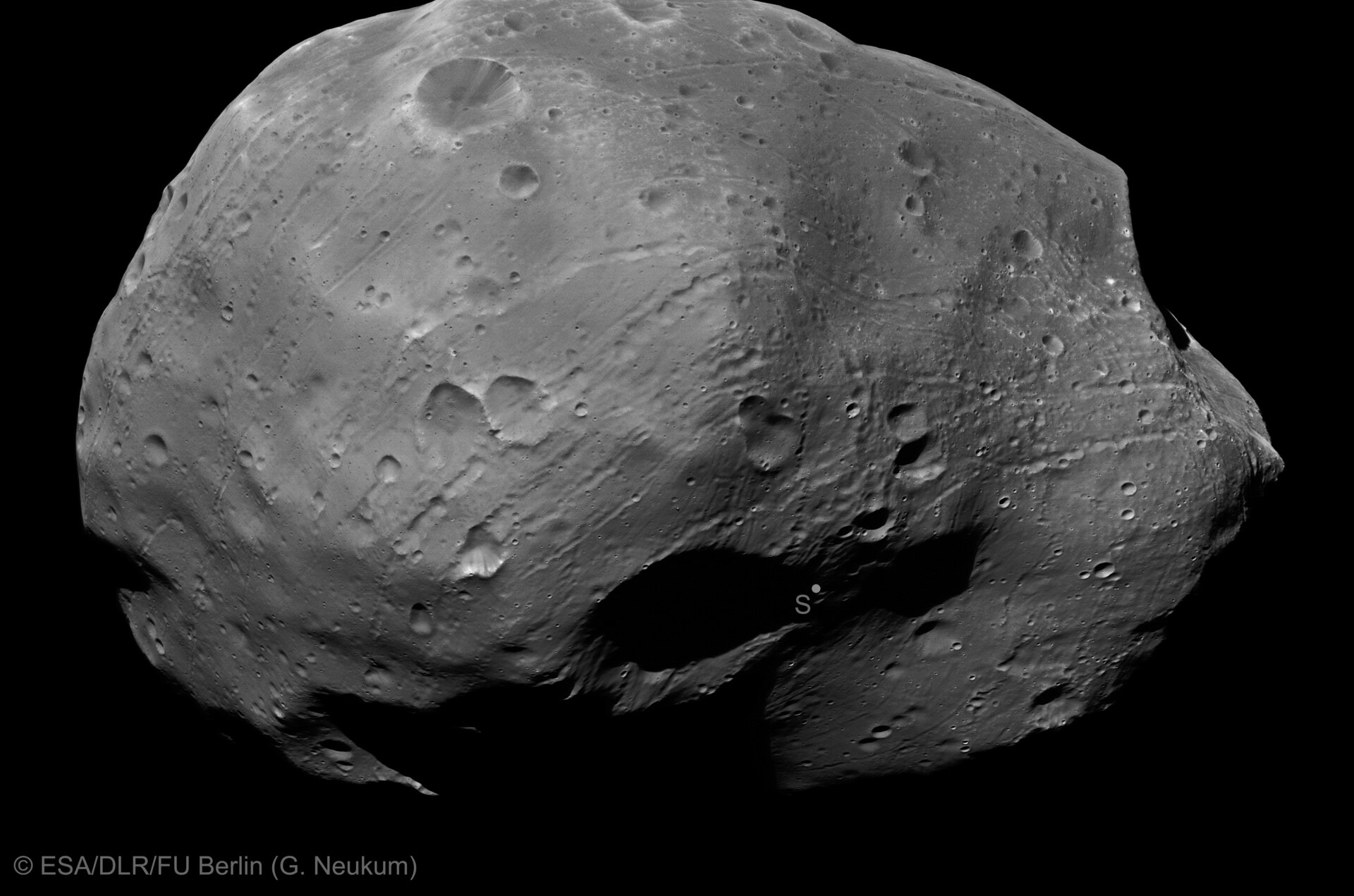
- Examining Mars’ moons Phobos and Deimos, with the revised mass and density data opening up the possibility that the interior of Phobos resembles a porous sponge.
- Identifying dried-up river valleys, traces of catastrophic floods, and buried glaciers.
- Contributing to the emerging picture of Mars as a once-habitable planet, with warmer and wetter epochs that may have once acted as oases for ancient martian life.
- Discovering localised aurora on Mars.
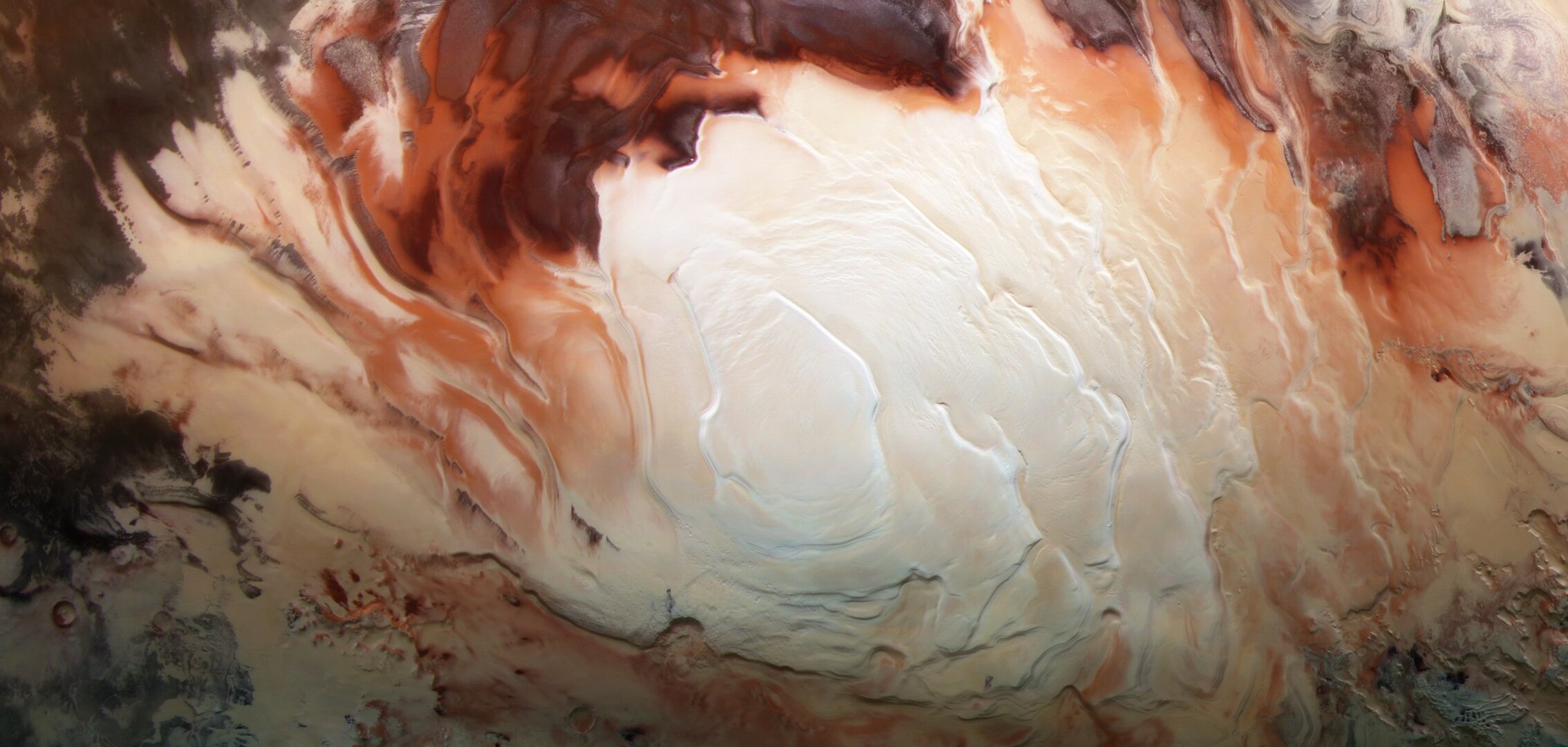
- Unearthing the quantity and composition of ice at the polar regions, finding that there is enough water ice in the south polar cap to create a global ocean 11-metres deep.
- Detecting volcanic activity as recently as 100 million years ago, leading to speculation that they may still be active today.
Mars Express' discoveries are paving the way for missions dedicated to hunting for signs of life on the planet, such as the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter and Rosalind Franklin rover mission.















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland