Observation of the atmosphere
Tracking trace gases
Trace gases in the troposphere and stratosphere are measured globally by the Sciamachy imaging spectrometer, yielding maps of air pollution such as carbon dioxide, methane and nitrogen dioxide. Nitrogen dioxide – a mainly man-made gas – can cause lung damage and respiratory problems. It also plays an important role in atmospheric chemistry because it leads to the production of ozone in the troposphere, the lowest part of the atmosphere.
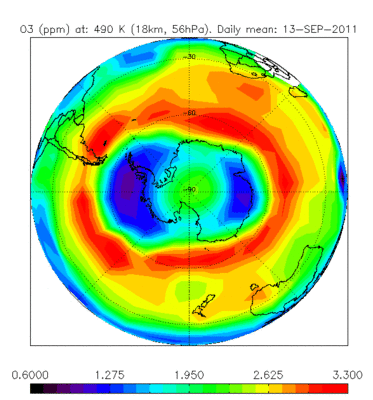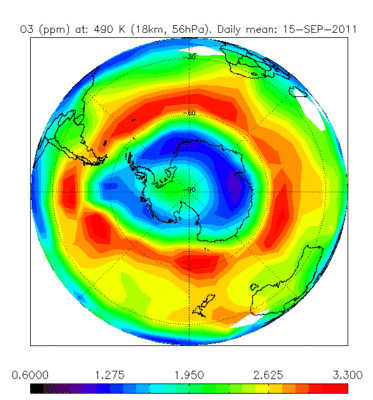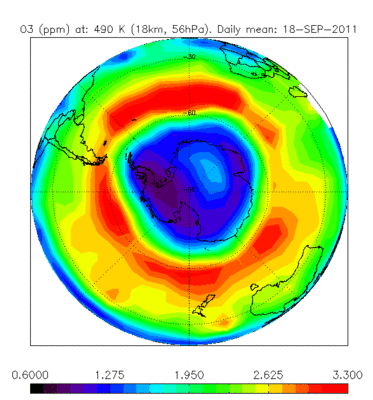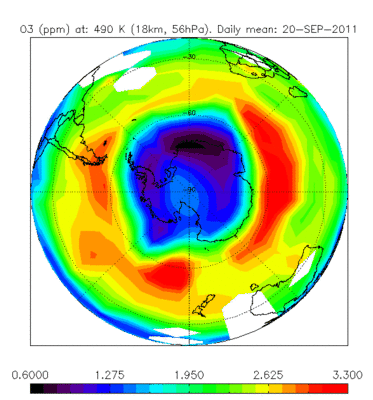
Ozone hole
Envisat’s Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric Sounding (MIPAS) monitors gases and pollutants. As one of three atmospheric instruments, it can map the levels of more than 20 trace gases, including ozone, as well as the pollutants that attack ozone. The sensor is particularly useful for tracking the ozone hole over the Antarctic. In April 2011 the lowest ever ozone concentration over the Arctic was observed by Envisat.















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland































