Introducing Φsat-2
Φsat-2, pronounced phisat-2, is a 6U cubesat that will further demonstrate the benefits of using Artificial Intelligence (AI) for innovative Earth observation.
This miniature satellite measures just 22 x 10 x 33 cm and carries a multispectral instrument that images Earth in seven different bands (plus a panchromatic band) in the visible to near-infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
AI applications carried on the satellite are then used in a number of ways, thereby demonstrating smarter ways of observing Earth.
For example, one of the AI applications automatically detects and discards any images acquired by the satellite where clouds obscure the view of Earth. Since this process is carried on the satellite, only clear and usable images are downlinked back to Earth.
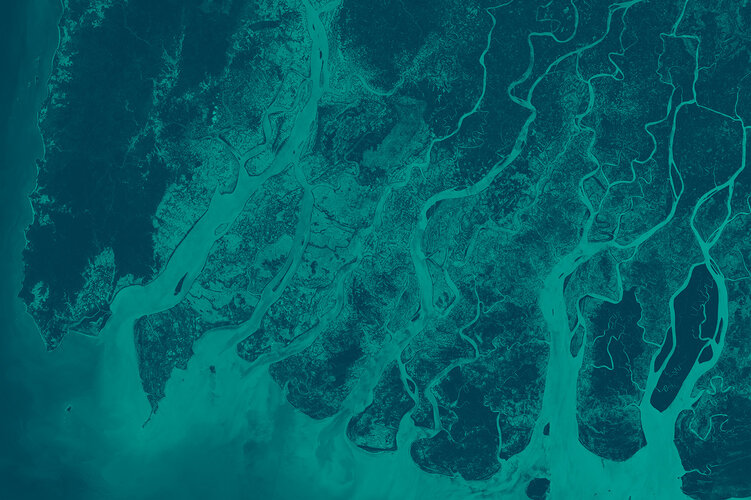
Another AI application can be used to convert satellite images into street maps. These maps can be used for emergency response teams to identify roads that are accessible – for example, when an area has been flooded or damaged by an earthquake. This application will first be demonstrated over Southeast Asia.
An additional AI application can be used to automatically detect marine vessels in predetermined areas to monitor activities such as illegal fishing.
AI is also used for deep image compression, thereby reducing the size of the files that are downlinked, and increasing the speed and the quantity of data downloads. This application will be first demonstrated over Europe and will focus on building detection.
As a result of the OrbitalAI Φsat-2 challenge, a further two AI applications have been added to the mission: one that focuses on marine pollution and one for wildfire detection.
Φsat-2, which shared its ride into orbit with other satellites, lifted off on 16 August 2024 on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from the Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, in the US.
The mission is developed by ESA with Open Cosmos as the prime contractor. The industrial consortium includes Ubotica, CGI, CEiiA, GEO-K and KP-Labs and SIMERA.















 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland



































