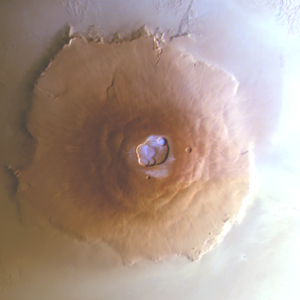
Newfound frost atop Olympus Mons
This high-resolution image shows newly discovered frost at the top of Olympus Mons, the tallest volcano not only on Mars but in the entire Solar System. The frost appears blue on the floor of the volcano’s caldera (summit crater) and around its northern rim. It is absent on the well-lit steep slopes seen on the left of this image.
This frost was recently discovered by ESA’s ExoMars and Mars Express missions. The researchers spotted frost on not only Olympus Mons but on the other Tharsis volcanoes of Arsia Mons, Ascraeus Mons and Ceraunius Tholus. This is the first time that water frost has been found near Mars’s equator, a part of the planet where it was thought improbable for frost to exist.
The landscape on the right side of the image is filled with wrinkle ridges that lie inside the caldera, while the rippled structures on the centre-left are collapsed caldera rim terraces.
The image is false colour, meaning that the colours shown here are not those that would be seen by the human eye. This is because the CaSSIS instrument onboard ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter is sensitive to near-infrared light (which is invisible to our eyes), and the image has stretched contrast to better show the details of the terrain. In this false-colour image the water ice frost appears blue. False-colour images are really useful for scientists, revealing more information than can be seen with the human eye. Read more on how CaSSIS constructs its blue-hued images, and how this allows us to explore the Red Planet.
The image resolution is 4.5 m/pixel, and the Local Solar Time is 7:11 AM.
[Image description: This rectangular slice of Mars shows the terrain atop Mars’s volcano Olympus Mons. Rippled, uneven, stepped terrain can be seen, with different illuminations. The right-hand side of the image is blue-toned, representing the newly discovered water ice frost.]