Accept all cookies Accept only essential cookies See our Cookie Notice

About ESA
The European Space Agency (ESA) is Europe’s gateway to space. Its mission is to shape the development of Europe’s space capability and ensure that investment in space continues to deliver benefits to the citizens of Europe and the world.
Highlights
ESA - United space in Europe
This is ESA ESA facts Member States & Cooperating States Funding Director General Top management For Member State Delegations European vision European Space Policy ESA & EU Responsibility & Sustainability Annual Report Calendar of meetings Corporate newsEstablishments & sites
ESA Headquarters ESA ESTEC ESA ESOC ESA ESRIN ESA EAC ESA ESAC Europe's Spaceport ESA ESEC ESA ECSAT Brussels Office Washington OfficeWorking with ESA
Business with ESA ESA Commercialisation Gateway Law at ESA Careers Cyber resilience at ESA IT at ESA Newsroom Partnerships Merchandising Licence Education Open Space Innovation Platform Integrity and Reporting Administrative Tribunal Health and SafetyMore about ESA
History ESA Historical Archives Exhibitions Publications Art & Culture ESA Merchandise Kids Diversity ESA Brand Centre ESA ChampionsLatest
Space in Member States
Find out more about space activities in our 23 Member States, and understand how ESA works together with their national agencies, institutions and organisations.
Science & Exploration
Exploring our Solar System and unlocking the secrets of the Universe
Go to topicAstronauts
Missions
Juice Euclid Webb Solar Orbiter BepiColombo Gaia ExoMars Cheops Exoplanet missions More missionsActivities
International Space Station Orion service module Gateway Concordia Caves & Pangaea BenefitsLatest
Space Safety
Protecting life and infrastructure on Earth and in orbit
Go to topicAsteroids
Asteroids and Planetary Defence Asteroid danger explained Flyeye telescope: asteroid detection Hera mission: asteroid deflection Near-Earth Object Coordination CentreSpace junk
About space debris Space debris by the numbers Space Environment Report In space refuelling, refurbishing and removingSafety from space
Clean Space ecodesign Zero Debris Technologies Space for Earth Supporting Sustainable DevelopmentLatest
Applications
Using space to benefit citizens and meet future challenges on Earth
Go to topicObserving the Earth
Observing the Earth Future EO Copernicus Meteorology Space for our climate Satellite missionsCommercialisation
ESA Commercialisation Gateway Open Space Innovation Platform Business Incubation ESA Space SolutionsLatest
Enabling & Support
Making space accessible and developing the technologies for the future
Go to topicBuilding missions
Space Engineering and Technology Test centre Laboratories Concurrent Design Facility Preparing for the future Shaping the Future Discovery and Preparation Advanced Concepts TeamSpace transportation
Space Transportation Ariane Vega Space Rider Future space transportation Boost! Europe's Spaceport Launches from Europe's Spaceport from 2012Latest

Weightless weak equivalence principle
Thank you for liking
You have already liked this page, you can only like it once!
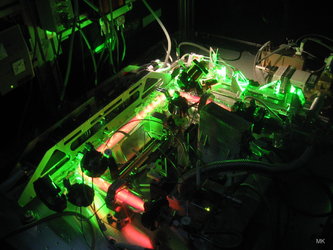
During ten seconds of weightlessness Brynle Barrett from the Laboratory of Photonics, Numerical Sciences and Nanosciences at the University of Bordeaux monitors an experiment to test the ‘weak equivalence principle’ – or why a feather in a vacuum falls as fast as a hammer.
To confirm that objects in free-fall behave universally, even at a microscopic level, a team of scientists used lasers to cool atoms to around –273°C. On Earth, atoms fall away from laser beams because of gravity. “In microgravity, atoms stay in the beams for much longer, so we get better data,” explains Brynle.
Parabolic flights are the only way to run such experiments on humans without leaving Earth’s atmosphere. Over the course of multiple roller-coaster flights at up to 45°, researchers find out more about the effects of gravity on experiments and improve equipment destined for space.
-
CREDIT
ESA -
LICENCE
ESA Standard Licence

'Zero-G' science

Parabolic flight experiment

Weightless in virtual reality

Air Zero-G flying high














 Germany
Germany
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Spain
Spain
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Norway
Norway
 The Netherlands
The Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Czechia
Czechia
 Romania
Romania
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
























